Yer Altı Kaynakları Dergisi Journal of Underground Resources
|
|
|
- Berk Korkmaz
- 8 yıl önce
- İzleme sayısı:
Transkript
1 Yer Altı Kaynakları Dergisi Journal of Underground Resources Yıl: 3 Sayı: 5 Ocak 2014 Year: 3 Number: 5 January 2014 ISSN:
2 MT Bilimsel Yer Altı Kaynakları Dergisi Journal of Underground Resources Derginin Adı MT Bilimsel İmtiyaz Sahibi MAYEB Madencilik ve Yer Bilimleri Basım Yayın Dağıtım Ltd. Şti. Genel Koordinatör Onur Aydın Yazı İşleri Müdürü Dış İlişkiler O. Çağım Tuğ İdari İşler Volkan Okyay Grafik Tasarım - Uygulama M. Anıl Tuğ anil@madencilik-turkiye.com İnternet Teknolojileri Bilgin B. Yılmaz bilgin@madencilik-turkiye.com Hukuk Danışmanı Av. Evrim İnal evrim@madencilik-turkiye.com Yayın İdare Merkezi Cd. (Eski 4. Cd.) Sk. (Eski 19. Sk.) Vadi Köşk Apt. No: 6/8 A. Öveçler ANK. Tel : +90 (312) Fax : +90 (312) info@mtbilimsel.com 6 Ayda Bir Yayınlanır Yerel Süreli Yayındır ISSN Ulusal Hakemli Dergidir Yayın Kurulu Baş Editör: C. Okay Aksoy (Dokuz Eylül Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) o.aksoy@mtbilimsel.com Yardımcı Editörler: Mahmut Yavuz Eskişehir Osmangazi Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü Vehbi Özacar Dokuz Eylül Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü Madencilik Türkiye Dergisi Temsilcisi Onur Aydın (Madencilik Türkiye Dergisi) onur@mtbilimsel.com Editörler (Alfabetik): Ali Sarıışık (Afyon Kocatepe Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Bahtiyar Ünver (Hacettepe Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Christopher Mark (Mine Safety & Health Admin., Coal Mine S. & H.) Çağatay Pamukçu (Dokuz Eylül Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Emin Candansayar (Ankara Üni,. Jeofizik Müh. Bölümü) Erol Kaya (Dokuz Eylül Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) G. Gülsev Uyar Aldaş (Ankara Üni., Jeofizik Müh. Bölümü) Güner Gürtunca (National Institute for Occupational Safety & Health) Hakan Başarır (Malatya İnönü Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Işık Yılmaz (Cumhuriyet Üni., Jeoloji Müh. Bölümü) İhsan Özkan (Selçuk Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Kadri Dağdelen (Colorado School Of Mines, Dept. of Mining Eng.) Kerim Küçük (Dokuz Eylül Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Melih Geniş (Zonguldak Karaelmas Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Melih İphar (Eskişehir Osmangazi Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Mustafa Ayhan (Dicle Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Nuh Bilgin (İstanbul Teknik Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Nuray Demirel (Orta Doğu Teknik Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Pinnaduva Kulatilake (The Univ. of Arizona, Dept. of Min. & Geo. Eng.) Raşit Altındağ (Süleyman Demirel Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Reşat Ulusay (Hacettepe Üni., Jeoloji Müh. Bölümü) Sair Kahraman (Niğde Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü) Samuel Frimpong (Missouri Univ. of Science & Tech., Dept. of Min. Eng.) Şevket Durucan (Imperial College, Mining And Environmental Eng.) Tim Joseph (Univ. of Alberta, School of Mining & Petroleum Eng.) Turgay Ertekin (The Pennsylvania State Univ., Petroleum & Nat. Gas Eng.) Turgay Onargan (Dokuz Eylül Üni., Maden Müh. Bölümü)
3 Yer Altı Kaynakları Dergisi Journal of Underground Resources Yıl:3 Sayı:5 Ocak 2014 ISSN: Year:3 Number:5 January 2014 İçindekiler Table of Contents Marilena Cardu, Pierpaolo Oreste Design Criteria for Production Blasting in an Underground Quarry: An Example of Application of the BDI Theory Patlatma Hasar İndeksi Teorisinin Bir Uygulama Örneği: Yeraltı Ocağında Üretim Patlatması için Tasarım Ölçütleri Iwona Jonczy Metallurgical Slags from Converter Furnace - Specificity of Their Phase and Chemical Composition Döner Fırından Metalurjik Curuflar - Faz ve Kimyasal Bileşimlerinin Belirliliği Marilena Cardu, Alessandro Giraudi, Vemavarapu M.S.R. Murthy, Bhanwar Singh Choudhary, A.K. Shukla Rock Characterization and Wire Performances for Dimension Stone Cutting by Diamond Wire Saw Elmas Tel Kesme ile Boyutlu Taş Kesimi için Kaya Karakterizasyonu ve Tel Performansı Ahmet Deniz Baş, Ersin Y. Yazıcı, Oktay Celep Geçmişten Günümüze Hidrometalurji Hydrometallurgy Over The Years...39
4
5 Yıl:3 Sayı:5 Ocak 2014 Year:3 Number:5 January 2014 Yer Altı Kaynakları Dergisi Journal of Underground Resources Araştırma Makalesi Design Criteria for Production Blasting in an Underground Quarry: An Example of Application of the BDI Theory Patlatma Hasar İndeksi Teorisinin Bir Uygulama Örneği: Yeraltı Ocağında Üretim Patlatması için Tasarım Ölçütleri Marilena Cardu 1 *, Pierpaolo Oreste 2 1 DIATI Politecnico, Torino, ITALY 2 IGAG National Research Council, Torino, ITALY *Responsible Author: marilena.cardu@polito.it Abstract Although not common, there are cases of underground quarries where the exploitation affects materials like limestone, when both technical and economic feasibility are guaranteed; the object of the present study is part of this case. The quarry is in operation since 1927: at present, the exploitation is carried out completely underground by sub-level stoping. The exploitation involves two levels, with 4 rooms at the upper level, and 9 rooms at the lower level. The need to comply with the required production respecting the desired grain size distribution implies the adoption of kg of explosives per blast. The vibrations, as well as the related unwanted effects, are then considerable, regardless of the timing system. The vibrations must therefore be reduced, through the analysis of the blasting pattern, a careful design and a proper performance of the blast. For this purpose, the theory of Blast Damage Index (BDI) was used: through the development of correlations between charge per delay, propagation velocity of p waves in the rock mass and peak particle velocity, it was possible to determine which pair minimum distance/maximum charge per delay is allowed. Key words: Blasting damage index, underground mining methods, vibrations, ppv. Özet Çok sık olmamasına rağmen, kireçtaşı gibi üretimi etkileyen malzemeler yeraltı ocaklarındaki bazı durumlarda hem teknik hem de ekonomik uygunluk garanti edildiğinde bu çalışmanın amacı bu durumun bir parçasıdır. Ocak 1927 den bu yana faaliyettedir: şu anda, üretim yeraltında tamamen arakatlı dolgu yöntemi ile yapılmaktadır. Üretim faaliyetleri 4 odalı üst kat ve 9 odalı alt kat olarak iki seviyeyi içermektedir. İstenilen tane boyut dağılımına uygun üretim için patlama başına kg patlayıcı madde kullanılması gereklidir. Zamanlama sistemine bakmadan, arzu edilmeyen etkilerinden dolayı titreşimler dikkate alınmalıdır. Bundan dolayı, titreşimler, dikkatli bir patlatma paterni tasarımı ve patlayıcının uygun performansı analiz edilerek azaltılmalıdır. Bu amaç için, gecikme başına şarj, kaya kütlesi içerisindeki p dalgalarının yayılım hızı ve en yüksek parçacık hızı arasındaki korelasyanların yardımıyla Patlatma Hasar İndeksi (PHİ) kullanılmıştır, en kısa mesafe / izin verilen gecikme başı en büyük şarj çiftinin belirlenmesi mümkün olmuştur. Anahtar kelimeler: Patlatma hasar indeksi, titreşimler, yeraltı üretim yöntemleri, ppv. 1
6 Cardu and Oreste 1. The Quarry and the Lime Plants The quarry is active since 1927, in the Bergamo province (Northern Italy), and feeds a large lime plant, with 4 vertical kilns, for a total production of burned lime of 350,000 t/y. Due to the burning loss (50%) and to the fines (<10 mm) that clog the kilns and therefore must be discarded before burning, a total yearly amount of 106 t/y of blasted rock (380,000 m 3 /y of rock in place) must be warranted. That means, for 220 worked days/y, an average daily production of 4,000 to 5,000 t. It has to be considered, however, that the burning process is continuous, and does not tolerate momentary shortages of feed. Two ample surge stockpiles, both of ready to burn rock and of blasted unprocessed rock have to be therefore warranted, to assure a constant feed even in the case of quarry production temporary stops (repairs, small delays in developments, displacements of semi-mobile machinery and so on). An appropriate daily production rate is 2,000 m 3 /d (in place). Primary and secondary crushing, sieving and washing plants are located underground, since the times of surface exploitation (Figure 1). A large (15,000 to 18,000 m 3 ) underground storage of crushed rock, to be used as surge stockpile, is under excavation. The reasons for the underground exploitation are explained in Figures 2 and 3. Limestone is abundant in the area, but only a member of the stratigraphic succession is locally suitable to the production of quicklime, represented by a bed m thick of very pure limestone. Other beds are either too rich of magnesia, or of silica, or both. As shown in Figure 2, the bed is sub-vertical, and to continue surface quarrying implies the removal of a growing amount of unsuitable limestone, for stability reasons (Oriard, 1982). This not only increases the ratio of the excavated useless rock to the pure limestone, as shown by the example of Figure 3 and, obviously, the cost of the exploitation, but is actually impossible, because there is not enough free space to dump the large amount of waste rock (Berta & Oth., 1999). On the contrary, underground exploitation can be favorably considered (Mancini & Oth., 2003): the limestone is sound in thick beds, RQD practically 100%, and wide stopes can be opened with the longer axis at right angle with the bedding, separated by pillars of adequate width. The percent recovery of the rock body is obviously low, with respect to a surface exploitation, but still warrants, within the permit limits, 20 years of production at the present rate. Figure 1. Front view of the old open pit exploitation; accesses to the underground (below) and the green (left) benches resulting from the exploitation are noticeable. Şekil 1. Eski açık ocak işletmesinin önden görünüşü; yeraltına geçişler (aşağıda) ve üretimden kaynaklanan yeşil (solda) basamaklar dikkat çekicidir. 2
7 Design Criteria for Production Blasting in an Underground Quarry: An Example of Application of the BDI Theory Figure 2. 3D scheme of the body, the surface exploitation and the underground exploitation; it is noticeable the increase of waste removal required to continue the surface exploitation (Mancini & Oth., 2005). Şekil 2. Cevherin 3 boyutlu şeması, açık işletme üretimi ve yeraltı üretimi; açık ocak üretiminin sürekliliği için pasa atımının arttırılması dikkat çekicidir (Mancini & Oth., 2005). Figure 3. Explanation of the physical limits of the surface exploitation. Vertical axis: amount of waste rock to be excavated; horizontal axis: amount of useful limestone excavated (cubic meters, for a vertical slice of unit thickness of the rock body). Şekil 3. Açık ocak üretiminin fiziksel sınırlarının açıklanması. Düşey eksen: kazılacak atık kayacın miktarı; yatay eksen: kazılacak faydalı kireçtaşının miktarı (metre küp, cevher kütlesinin birim kalınlığının düşey bir dilimi için). 2. Mining Method and Rock Stability Problems The method is a sublevel stoping, with haulage by conveyor belts: the blasted rock is taken at the draw-points by LHD machines and transferred to a mobile crusher, feeding the conveyor belt ore passes system for the upper 4 stops; the lower stopes (5 to 13) are exploited in the same way, but the haulage is effected by LHD + dumper tracks, and the primary crusher is installed in a fixed position. A general plan of the mine is shown in Figure 4; presently, only 5 of the 13 stopes have been exploited. The mechanical strength data of the limestone have been obtained from extensive coring (Table 1). The geomechanical quality of the rock mass is good, according to the surveys effected in the previous surface exploitation and in development tunnels. Some 3
8 Cardu and Oreste karstic cavity of small extent has been crossed by the development works, in the upper levels; no groundwater problems, however, have been found, nor are expected, being the water table dictated by the river bed (290 m a.s.l), while the foreseen exploitation develops at altitudes over 305 m a.s.l. The mine has been designed according to the same principles followed in designing a multi-stage building in masonry. Pillars are considered as walls subjected to vertical loads (the rock cover plus their own weight) and to horizontal loads (the unbalanced lateral thrust of the self supporting vaults connecting the pillars); a thickness of 2 m of rock adjacent to the surface of the walls is considered as contributing load but not strength (the analogous of the plaster coating of a wall), being presumably cracked by the immediate proximity of the blasts. The admissible tensile stress is considered 0, the admissible compression stress is 1/4 of the minimum C0 measured on the cores, hence 25 MPa. Pillars are therefore verified for stability as walls subjected to eccentric vertical load: if the resultant vertical force falls within the median third of the resisting horizontal section, the whole section (apart from the supposed damaged layer) has bearing function, if falls outside the median third, tensile stresses can occur and the resisting section is accordingly reduced in the stability calculations. A maximum slenderness ratio of 2.5 has been set for the pillars. The vaults connecting the pillars are calculated according to the natural self supporting arch criterion (Bello 1977); a rock cover of at least 30 m above the self supporting arc top has been set. Figure 4. 3D view of the quarry, at the end of the exploitation (Mancini & Oth., 2005). Şekil 4. Üretimden sonra ocağın üç boyutlu görüntüsü (Mancini & Oth., 2005). Table 1. Mechanical data of the limestone. Çizelge 1. Kireçtaşının mekanik verileri. Specific gravity 2.67 t/m 3 C 0 Over 140 MPa (min 100 MPa) T 0 (Brazilian) Over 6 MPa The access and drilling tunnels have a cross section of m 2 (haulage and access) and 25 m 2 (drilling), allowing for an easy circulation and operation of the machinery; the maximum grade has been set at 15 %. Ore passes are drilled by raise borer, 3 to 5 m in diameter, inclined by 200 with respect to the vertical. Apart from occasional bolting, no rock support is needed up to now. The stability of the pillars is monitored by means of extensometers installed permanently in selected points. 4
9 Design Criteria for Production Blasting in an Underground Quarry: An Example of Application of the BDI Theory 3. Exploitation The first stope has been exploited using one drilling tunnel per sub-level, say 3 drilling tunnels per stope, as shown in Figure 5, right. This arrangement was chosen with the aim of minimizing the incidence of the development work and of retaining some possibility of reducing the width of the stope, in the case of an unforeseen reduction of the self supporting ability of the roof. Some drawbacks became apparent during the exploitation (anyhow, successfully accomplished): slotting is difficult and time consuming, the side walls of the open stope are often very irregular due to poor or excessive breakage at the toe of the holes, the round includes a great number of long upward holes, difficult to drill and to charge. Though being the results still acceptable (see Figure 6), starting from the stope n. 2 a different scheme, with two drilling tunnels in each sub-level, is adopted (Figure 5 left), which implies a greater incidence of the preparatory work but provides better control of the pillar size and strength, and other changes (to increase the sub-level spacing, and the size of the production blasts) are under study. Present production blasts are designed for rock volumes of 2,700 to 3,000 m 3 each. The basal collecting trough is excavated with smaller blasts, some rounds in advance with respect to production, as shown in the same figure. Draw points are spaced by 20 m. Blasted rock in collected by 7 9 m 3 LHD loders, carried to the mobile crusher, and fed to the belt-ore passes system. The average volume of a stope is 500,000 to 550,000 m 3 (being the width 30 m, the length 180 m, the height 110 m), say 1.4 years of production. That means that in the same time a new stope must be ready (the drilling tunnels prepared and the slot opened), a pace that proved to be maintainable. Total workforce amounts to 15 (partly hired from an external contractor), and machinery comprises 2 jumbos, 1 SOLO drill (for production drilling), 2 TORO LHD (7 m 3 and 9 m 3 ), 1 mobile crusher, belting (as explained, the haulage system is due to be changed). Figure 5. Right: exploitation with 3 sub levels, one drilling tunnel per sublevel; left: same, with 2 drilling tunnels per sublevel. Şekil 5. Sağ: 3 arakatın üretimi; sol: aynı, her arakat için 2 delik delme tüneli. 5
10 Şekil 5. Sağ: 3 arakatın üretimi; sol: aynı, her arakat için 2 delik delme tüneli. Cardu and Oreste Figure 6. Representation of the results obtained from a production blast at stope n. 1. Şekil 6. 1 numaralı katlar arasında üretim patlatmasından elde edilen sonuçların sunumu. 4. The Blast Damage Index Figure 6. Representation of the results obtained from a production blast at stope n. 1. The BDI (Yu & Vongpaisal, 1996) can be considered as the reciprocal of a safety factor, and Şekil 6. 1 numaralı katlar arasında üretim patlatmasından elde edilen sonuçların sunumu. is represented as the ratio between dynamic stress induced and rock strength. Denoting by: V 4. The Blast Damage Index = vector sum of the three components of peak particle velocity (m/s); d = density of the rock The BDI (Yu & Vongpaisal, 1996) can be considered as the reciprocal of a safety factor, and is represented (kg/dm 3 ); c as = speed the ratio of compression between dynamic waves stress in the induced rock-mass and (m/s); rock strength. K S = site Denoting quality constant, by: V = vector variable sum between of the three 0 and components 1 and dimensionless, of peak particle the stress velocity induced (m/s); in d the = rock density is expressed of the rock as (kg/ the dm 3 ); c = speed of compression waves in the rock-mass (m/s); K S = site quality constant, variable between product of 0 and the 1 factors and dimensionless, V, d and c, while the the stress rock induced strength in is the the rock product is expressed of the dynamic as the product tensile of strength the factors of the V, d rock, and c, the while site the quality rock constant, strength is and the a product correction of the factor; dynamic then, tensile the index strength of of the rock, the site quality constant, and a correction factor; then, the index of damage can be damage can be expressed as a function of six parameters: expressed as a function of six parameters: BDI = V d c [1] T K S 10 6 On the basis of tests carried out to determine the dynamic tensile strength of different types On the basis of tests carried out to determine the dynamic tensile strength of different types of of rock, Mohanty (1987) found that the ratio between the compressive strength and the dynamic rock, tensile Mohanty strength (1987) varies found between that the 3.2 ratio and between 3.9. The the proportion compressive between strength the and dynamic the dynamic tensile strength tensile strength and the tensile varies strength between determined 3.2 and 3.9. with The the proportion Brazilian test, between instead, the varies dynamic between tensile a minimum of 1.6 and a maximum of 9.3. The results of a series of uniaxial and triaxial compressive tests on samples obtained from core surveys carried out at the quarry show that the value of uniaxial compressive strength is 141 6
11 implies an anisotropic behaviour of the rock-mass and for this reason it was decided to assign an implies average an anisotropic value of dynamic behaviour tensile of the strength rock-mass of and about for 29 this MPa. reason The it was uniaxial decided compressive to assign Design Criteria for Production Blasting in an Underground Quarry: strength an average is one value of of the dynamic parameters tensile needed strength to assess of about RMR An 29 (Rock Example MPa. Mass of The Application Rating) uniaxial of and the compressive BDI hence Theory the site strength quality is one constant of the K parameters needed to assess RMR (Rock Mass Rating) and hence the S. For the site under consideration, a RMR= 69 parallely to the layers site MPa, and quality RMR= constant while the 81 perpendicularly K Brazilian S. For the tensile were site under strength found, consideration, is and over thus 6 MPa. the K a RMR= 69 parallely to the layers The S values rock is can a very be fixed pure as limestone, 0.81 and stratified 0.69 and RMR= respectively. in banks, 81 perpendicularly with good strength were found, characteristics and thus and, the therefore, K S values a can value be of fixed 3.9 it as is assumed 0.81 and as 0.69 the respectively. ratio between compressive and dynamic tensile strength. The layering implies an anisotropic behaviour of the rock-mass and for this reason it was decided to assign an average value of The dynamic density tensile of the strength intact rock of about is kg/dm MPa. 3, while The uniaxial the rock-mass compressive shows strength an average is one value of the of parameters needed to assess RMR (Rock Mass Rating) and hence the site quality constant KS. For 2.65 The density the kg/dm site under 3. of The the consideration, in-situ intact compression rock is 2.7 kg/dm a RMR= waves 3, 69 parallely speed while perpendicularly the rock-mass shows to the layers and to the an RMR= layers average value of 81 is perpendicularly and 5,800 m/s 2.65 a were kg/dm higher found, 3. The value, and in-situ i.e. thus compression the seismic K S values velocity waves can be speed fixed in the perpendicularly as intact 0.81 and rock 0.69 (about to respectively. the 6,300 layers m/s) is 5,800 is fixed m/s parallely and a higher to the value, stratification. i.e. the seismic velocity in the intact rock (about 6,300 m/s) is fixed The density of the intact rock is 2.7 kg/dm 3, while the rock-mass shows an average value of 2.65 parallely to the stratification. kg/dm 3. The in-situ compression waves speed perpendicularly to the layers is 5,800 m/s and a higher PPP refers value, to i.e. the the vector seismic sum velocity of the three in the orthogonal intact rock components (about 6,300 of the m/s) particle is fixed velocity. parallely The to the PPP stratification. level refers of vibration to the vector varies considerably sum of the three depending orthogonal on whether components a cylindrical of the particle or a spherical velocity. charge The PPP is level considered; refers of vibration to the in the vector varies first sum considerably case, of the the following three depending orthogonal formula on whether components was found: a cylindrical of the particle or a spherical velocity. charge The level is considered; of vibration in the varies first considerably case, the following depending formula on whether was found: a cylindrical or a spherical charge is considered; in the first case, the following formula was found: V V m R = K m [2] 1 / 2 WR = K 1 / 2 [2] W and, in the second: and, in in the second: m R = K m [3] 1 / 3 WR = K 1 / 3 [3] V V In the following, W the values of ppv as a function of scaled distance will be examined, obtained in using which: which: both V=vector V=vector the square sum sum root of the of and the three the three cubic components components root of the of peak charge of particle peak in kg, particle velocity, while velocity, the expressed charge expressed will in (mm/s); still be in W=mass (mm/s); in which: of W=mass V=vector the charge of the sum (kg); charge of K, the m=constants (kg); three K, components depending m=constants of on depending peak the site; particle R=the on the velocity, distance site; R=the between the considered concentrated in the barycentre and, accordingly, the distances expressed distance in in m charge and the measuring point (m). between (mm/s); will those W=mass the charge between of and the the the charge barycentre measuring (kg); and K, point the m=constants (m). point of measurement depending on and the the site; mass R=the of the distance charge In between will the following, the the charge the per and values delay. the of measuring The ppv data a point examined function (m). of are scaled related distance to 62 production will be examined, blasts. As obtained for the using both the square root and the cubic root of the charge in kg, while the charge will still be considered site under as study, concentrated the layered in the stratification barycentre of and, limestone accordingly, affects the the distances behaviour expressed of rock-mass: in m will it be can those be noticed, between in the fact, barycentre a different and arrangement the point of of measurement data collected and parallely the mass and of perpendicularly the charge will be the charge per delay. The data examined are related to 62 production blasts. As for the site under to the study, layers; the an layered example stratification is shown of in limestone Figure 7. affects With regard the behaviour to the analysis of rock-mass: that takes it can into be noticed, account in the fact, square a different root, the arrangement following of formulas data collected were found, parallely respectively and perpendicularly considering to the layers; an example is shown in Figure 7. With regard to the analysis that takes into account the parallel (Eq. 4) and perpendicular (Eq. 5) direction: square root, the following formulas were found, respectively considering the parallel (Eq. 4) and perpendicular (Eq. 5) direction: ppv = ppv = R W 1/ 2 R W 1/ [4] [5] 7
12 Cardu and Oreste Figure 7. ppv - scaled distance calculated through the cubic root of the charge (data refer to the two directions: parallel - blue line - and perpendicular - red line - to the layers). Şekil 7. ppv - şarjın küp kökü üzerinden hesaplanan ölçekli mesafe (veri iki boyutu işaret etmektedir: paralel - mavi If the çizgi analysis - ve dik doğrultu is performed - kırmızı using çizgi - the katmanlar). cubic root of the charge, the following results were obtained, with coefficients and exponents higher than in the previous case, respectively If the analysis is performed using the cubic root of the charge, the following results were obtained, considering with coefficients the parallel and (Eq. exponents 6) and perpendicular higher than in (Eq. the previous 7) direction: case, respectively considering the parallel (Eq. 6) and perpendicular (Eq. 7) direction: ppv = ppv = R W 1/ 3 R W 1/ [6] [7] The interpolation of the data must be corrected in order to obtain a ppv-ds law that is valid and cautionary The interpolation most of cases: the analysis data must was be performed corrected in which order allowed to obtain to find, a ppv-ds fixed the law exponent that is valid m, the and coefficient cautionary K in by most which cases: the curve analysis would was encompass performed 90% which of the allowed values. It to was find, set fixed a confidence interval of 90%, taking the risk that the 10% of the pairs of values ppv-ds could be above the the exponent straight m, line the that coefficient represents K by the which maximum the curve value would of the encompass range. 90% of the values. It was set a confidence interval of 90%, taking the risk that the 10% of the pairs of values ppv-ds could be above the straight line that represents 8the maximum value of the range.
13 Design Criteria for Production Blasting in an Underground Quarry: An Example of Application of the BDI Theory An example of graph, obtained using the cubic root of the charge and referring to the measurements taken parallely to the layers, is provided in Figure 8. Figure 8. Peak particle velocity - DS, calculated with the cubic root of the charge and parallely to the layers. Dotted line: mean value; solid line: upper value. Şekil 8. En yüksek parçacık hızı - şarjın küp kökü üzerinden hesaplanan DS ve katmanlara paralel. Noktalı çizgi: ortalama değer; sürekli çizgi: üst değer. The data lead to reasonable results, as it is logical that the rock-mass, characterized by good mechanical characteristics, present a strongly anisotropic behaviour along the two directions perpendicular and parallel to the layers, with a good propagation and low values of ppv behind the charge in the first case and a strong dissipation in the second, combined with high ppv when scaled distances are low. Figures 9, 10 show the trend, along the two directions, of ppv as a function of scaled distance, obtained respectively with the square and the cubic root of the charge. Figure 9. ppv - DS calculated with the square root of the charge. Şekil 9. ppv - şarjın kare kökü üzerinden hesaplanan DS. 9
14 Cardu and Oreste Figure 10. ppv - DS calculated with the cubic root of the charge. Şekil 10. ppv - şarjın kare kökü üzerinden hesaplanan DS. 4.1 Determination of BDI For each of the solutions is taken into account the behaviour of the rock along the two perpendicular directions, so as to ensure a good representation of the rock mass, which is anisotropic; there With are regard no tunnels to one or of underground the infinite voids directions that are parallel not perpendicular to the layering, or parallel which to can the stratification, then is not considered the behaviour of the rock-mass along intermediate directions: thus, be either vertical or horizontal, the following values have been assumed: rock density d: 2,670 kg/m 3 ; for the assessment of damage, an area along one of the tunnels that is closest to the blast can be still speed be of found, compression to assess waves the effects c: 5,700 of damage m/s; dynamic to the structure. tensile strength T: 25 MPa; site quality constant K S : With regard to one of the infinite directions parallel to the layering, which can be either vertical or horizontal, the following values have been assumed: rock density d: 2, 670 kg/m 3 ; speed of compression With regard to waves the direction c: 5,700 m/s; perpendicular dynamic tensile to the layering, strength T: the 25 following MPa; site values quality were constant assumed: KS: rock density d: 2,670 kg/m 3 ; speed of compression waves c: 6,300 m/s; dynamic tensile With strength regard T: 36 to MPa; the direction site quality perpendicular constant Kto S : the layering, the following values were assumed: rock It is density therefore d: possible 2,670 kg/m to 3 express ; speed of the compression relationship waves between c: 6,300 BDI m/s; and dynamic ppv as linear, tensile with strength only T: 36 MPa; site quality constant KS: one constant which encloses all the fixed values: the strong differences in the behaviour of the It rock is therefore led to investigate possible to express a law which the relationship varies with between the direction BDI and ppv considered: as linear, it with is therefore only one constant which encloses all the fixed values: the strong differences in the behaviour of the rock led determined to investigate a constant a law for which the varies parallel with direction the direction and a constant considered: for the it is perpendicular therefore determined direction, a constant according for to the parallel following direction expressions: and a constant for the perpendicular direction, according to the following expressions: ppv BDI par = = ppv [8] ppv BDI perp = = ppv [9] At this point, by imposing the maximum BDI which is thought to be achieved respecting the structures, At this point, a limit by to imposing the peak the particle maximum velocity BDI can which be established thought and to therefore, be achieved being respecting available the relations ppv-ds, a couple minimum distance/maximum charge not to be exceeded can be found. structures, a limit to the peak particle velocity can be established and therefore, being available the relations ppv-ds, a couple minimum 10 distance/maximum charge not to be exceeded can be found.
15 Design Criteria for Production Blasting in an Underground Quarry: An Example of Application of the BDI Theory This pair of values is uniquely identified by a value of DS, scaled distance: by increasing the load, the scaled distance decreases in reason of the square root of the charge, then the limit is constituted by a value of maximum charge, whereas the decrease of the actual distance implies that the DS also decreases, then a limit value for the distance is constituted by a minimum below which we should not go down. The relationships (for the directions perpendicular and parallel to the layers) that link the BDI to ppv are represented in the graph of Figure 11. Figure 11. Correlation between BDI and ppv in the direction perpendicular (BDI = ppv) and parallel (BDI = ppv) to the layers. Şekil 11. Dik doğrultu yönündeki BDI ve ppv arasındaki korelasyon (BDI = ppv) ve katmanlara paralel yöndeki (BDI = ppv). In the case examined, for which a BDI threshold of was proposed, the ppv max in the two directions being known, the scaled distances can be evaluated (Table 2). Figures 12 and 13 provide an example of the relationship between distance and charge per delay, with BDI = 0.250, having adopted a scaled distance respectively calculated with the square and the cubic root of the charge. These graphs can be used to calculate, known the maximum charge per delay, the minimum distance from the charge to be observed, or, once the distance is known, to determine the maximum charge per delay that can be used in a given blast. 11
16 maximum charge per delay that can be used in a given blast. Cardu and Oreste Table 2. Maximum values of DS obtained. Çizelge 2. DS den elde edilen en yüksek değerler. DS Dir. Dir. BDI (-) ppv BDI (mm/s) (-) DS ppv (m/kg (mm/s) 1/2 1/2 ) DS (m/kg 1/2 ) 2 Par. Par Perp. Perp DS Dir. Dir. BDI (-) ppv BDI (mm/s) (-) DS ppv (m/kg (mm/s) 1/2 1/2 ) DS (m/kg 1/2 ) 3 Par. Par Perp. Perp Table 2. Maximum values of DS obtained. Çizelge 2. DS den elde edilen en yüksek değerler. Figure 12. Representation of R (distance, m) v/ W (charge, kg) when the scaled distance is calculated with the square root of the charge. Şekil 12. Ölçekli mesafe şarjın kare kökü ile hesaplandığında R nin gösterimi (mesafe, m) v/ W (şarj, kg). Figure 13. Representation of R (distance, m) v/ W (charge, kg) when the scaled distance is calculated with the cubic root of the charge. Şekil 13. Ölçekli mesafe şarjın küp kökü ile hesaplandığında R nin gösterimi (mesafe, m) v/ W (şarj, kg). 5. Conclusions The underground exploitation is not intended to compete with surface exploitation, when both are practicable, due to the higher development costs. In the case, however, the underground exploitation was the only way to avoid the closure of the plant, and the higher costs of the raw rock ton at the kiln, which can be quantified as 100 % more than in previous surface production, 12
17 Design Criteria for Production Blasting in an Underground Quarry: An Example of Application of the BDI Theory can be accepted when balanced to the cost of closing or transferring the production of lime or supplying the row rock from another quarry. From monitoring and observation of the damage caused by production blasts, which involve large amounts of explosive, the following conclusions can be drawn: - The damage observed is of the same order of magnitude as predicted by the theory of Blast Damage Index; - The values of BDI expected vary from a minimum of zero (only theoretically, because BDI = 0 means that the dynamic stress is absent, which is impossible!) to a maximum of 2, which corresponds to a damage which generally determines the closing of the accesses and the abandonment of the area: for this maximum value of BDI, each intervention recovery is fruitless, or so inconvenient from the economical point of view, that does not deserve to be taken into consideration; - The levels of damage are described by Yu and Vongpaisal (1996) in terms of tolerable damage: in the case of the Kidd Creek mine (Yu & Quesnel, 1984)., in fact, and also for the underground quarry examined, collapses and detachments due to blasting (Persson & Holmberg, 1994).occur when no one is in potentially hazardous zones: for tolerable damage is intended, therefore, a repairable damage with a tolerable cost; - the simple limitation of the ppv value below the limit set by a rule, leaves only the possibility of reducing the charges used (in practice, to slow down the production) while, at least in principle, it is possible to comply with a limit value of BDI also working on the denominator of the ratio, i.e. improving the rock quality. References Bello, A., Simplified method for stability analysis of underground openings. Proc. 1st Int. Symp. Rockstone 77, Stockholm, Mancini, R., Cardu, M. and Piovano V., How the underground quarry design evolves from feasibility study to operation: an analysis of two Italian cases. Proc. Int. Symp. IMBS, Istanbul, Mancini R., Cardu M., Piovano V. and Zammarian L., Sublevel stoping at a large underground quarry: the improvement of the development and exploitation design. 14th International Symposium on Mine Planning and Equipment Selection-MPES, Banff, Canada. (pp ). ISBN/ISSN: Singhal, Fytas, Chiwetelu Ed. Berta G., Nasca F., Tamburi M. and Cian P. (1999). Impiego di esplosivo per la coltivazione in sotterraneo di una roccia calcarea, p , Proc. Congr. Attuabilità e Problematiche degli Scavi in Galleria in Italia. A.N.I.M Verona, Italia. Mohanty B., Strength of rock under high strain rate loading conditions applicable to blasting, p , proceedings of the 2nd Symposium on Rock Fragmentation by Blasting. Keystone, U.S.A. Oriard L.L., Blasting effects and their control, Underground Mining Methods Handbook, W.A. Hustrulid Ed. Society of Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration, p Persson D.A., Holmberg R. and LEE J., Rock Blasting and Explosives Engineering, CRC press. New York, U.S.A. Yu T.R. and Vongpaisal S., New blast damage criteria for underground blasting, CIM bulletin, vol. 89 n 998. Yu T.R. and Quesnel W.J Ground control at Kidd Creek Mine, p , Proceedings of Geomechanics Applications in Underground Hard-rock Mining, W.G. Pariseau Ed. 13
18
19 Yıl:3 Sayı:5 Ocak 2014 Year:3 Number:5 January 2014 Yer Altı Kaynakları Dergisi Journal of Underground Resources Araştırma Makalesi Metallurgical Slags from Converter Furnace - Specificity of Their Phase and Chemical Composition Döner Fırından Metalurjik Curuflar - Faz ve Kimyasal Bileşimlerinin Belirliliği Iwona Jonczy 1 * 1 Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Mining and Geology, Institute of Applied Geology, Gliwice, POLAND *Responsible Author: iwona.jonczy@polsl.pl Abstract Metallurgical slags, which come into being as a secondary product of steel making, are more and more often used in different economy fields. In Poland there is a search for solutions to close down dumping grounds of metallurgical wastes and to manage the slags which come into being during the current production to avoid their long-term storage. This work must be preceded by multidirectional research, among which analyses of phase and chemical compositions of slags play an important role. In the mineral composition of the slags, apart from crystalline components, the presence of glaze and iron metallic precipitations was noticed. The degree of crystallization of individual components was different depending on the speed of cooling an alloy, which also allowed us to distinguish their different microstructures. Chemical composition of the metallurgical slags is variable and depends on: the type of the used charge material, fluxes, refining additives and a used melt technology. Nevertheless in all tested slags iron was presented in the largest quantities. Key words: Metallurgical slag, metals, phase composition. Özet Çelik üretiminde ikincil ürün olarak elde edilen metalurjik cüruflar farklı alanlarda ekonomik olarak çok daha fazla sıklıkla kullanılmaktadır. Polonya da metalurjik cürufların zemine dökülerek kapanmasına çözüm bulabilmek ve uzun dönem depolanmalarından kaçınılması için mevcut üretim sürecinde oluşan cürufların düzenlenmesi için araştırmalar yapılmaktadır. Bu çalışma cürufların kimyasal bileşimleri ve fazlarının analizi arasında önemli bir rol oynayan çok yönlü bir araştırma ile ilerlemelidir. Cürufların mineral bilişimlerinde kristal bileşimlerinden ayrı olarak camlaşmanın ve demir metalik çökelmenin varlığına dikkat edilmiştir. Bileşenlerin ayrı ayrı kristalleşme dereceleri farklı mikro yapılarının aynı zamanda ayrılmasında izin veren soğuma hızına bağlı olarak farklılık göstermiştir. Metalurjik cürufların kimyasal bileşimi değişkendir ve kullanılan şarj malzemesinin tipine, eritkenlere, rafine katkılarına ve kullanılan eriyik teknolojisine bağlıdır. Bulunla birlikte, test edilen bütün cüruflarda, demir büyük miktarlarda bulunmuştur. Anahtar kelimeler: Metalurjik cüruf, metaller, faz bileşimi. 15
20 Jonczy 1. Introduction Upper Silesia is one of the best industrialized regions in Poland (south part of Poland). The beginnings of mining and smelting have been dated here on the Middle Ages. Beside coal mining, iron and steel industry has become one of the most developed industries in this region. But on the other hand iron and steel industry became especially problematic, because of considerable amounts of wastes - mainly metallurgical slags, coming into being during production. In the past slags were gathered on the dumps. Presently, in view of widely accepted pro-ecological policy, attention has been drawn to the possibility of using metallurgical slags, both the slag collected on dumps and the slags generated by ongoing production processes, as a secondary material. Technical researches of slags have shown that they may be used to produce aggregates for highway engineering. There are also numerous researches carried out in order to acquire metals from metallurgical slags. All these activities must be preceded by multidirectional laboratory analyses connected, among others, with learning the chemical and phase composition of slags (Cioroi et al. 2010; Jonczy 2007, 2011; Jonczy et al. 2012; Mateus et al. 2011; Rai et al. 2002). Moreover the study of slag are already carried out at the stage of their forming inside of the blast furnace (Kudrin 2007; Kozhukhov 2013). Based on the detailed studies, connections of metals with slag phases and possibilities of their migration from slags during their utilization, could be determined. In this article there is presented a characterization of a chemical and mineralogical composition of metallurgical slags from one steel works in Poland. The research was carried out on 4 types of slag originating as a secondary product in a converter furnace during 4 different cycles of smelting. The differences between successive cycles are connected with variable conditions of cooling a slag alloy and with a slightly different character of a furnace charge which is connected first of all with a various amounts and different type of scrap added to the charge. Slags analyzed macroscopically are similar to one another, they are characterized by black color and they are brittle and porous. 2. Research methods Chemical composition of slags was determined in the Activation Laboratories Ltd. ACTLABS in Canada using the TD-MS and TD-ICP methods. Spectral analysis in microareas was carried out at the Institute of Non-ferrous Metals at Gliwice (Poland) and the X-ray analysis at the Institute of Ceramics and Building Materials department also at Gliwice. The research with the application of scanning microscopy was carried out at the Scanning Microscopy Laboratory of Biological and Geological Sciences of the Department of Biology and Earth Sciences of the Jagiellonian University in Kraków (Laboratory at the Institute of Geological Sciences). Microscopic observations in transmitted light were made at the Institute of Applied Geology of the Faculty of Mining and Geology of the Silesian University of Technology in Gliwice (Poland). 3. Results Metallurgical slags could contain a considerable amount of metals, so it is very important to control their concentration, especially when we use slags as a secondary material. In the chemical composition of the analyzed metallurgical slags there dominate Fe (14,14-20,00%), in the second place is Mn whose concentration in all samples is similar - ~1% (tab. 1). Ni, Ti and Pb appear in changeable amounts and their increased concentration was noticed in the sample No 2. In the sample No 3 the content of Cr increases, whereas in the sample No 16
WEEK 11 CME323 NUMERIC ANALYSIS. Lect. Yasin ORTAKCI.
 WEEK 11 CME323 NUMERIC ANALYSIS Lect. Yasin ORTAKCI yasinortakci@karabuk.edu.tr 2 INTERPOLATION Introduction A census of the population of the United States is taken every 10 years. The following table
WEEK 11 CME323 NUMERIC ANALYSIS Lect. Yasin ORTAKCI yasinortakci@karabuk.edu.tr 2 INTERPOLATION Introduction A census of the population of the United States is taken every 10 years. The following table
Yüz Tanımaya Dayalı Uygulamalar. (Özet)
 4 Yüz Tanımaya Dayalı Uygulamalar (Özet) Günümüzde, teknolojinin gelişmesi ile yüz tanımaya dayalı bir çok yöntem artık uygulama alanı bulabilmekte ve gittikçe de önem kazanmaktadır. Bir çok farklı uygulama
4 Yüz Tanımaya Dayalı Uygulamalar (Özet) Günümüzde, teknolojinin gelişmesi ile yüz tanımaya dayalı bir çok yöntem artık uygulama alanı bulabilmekte ve gittikçe de önem kazanmaktadır. Bir çok farklı uygulama
Ege Üniversitesi Elektrik Elektronik Mühendisliği Bölümü Kontrol Sistemleri II Dersi Grup Adı: Sıvı Seviye Kontrol Deneyi.../..
 Ege Üniversitesi Elektrik Elektronik Mühendisliği Bölümü Kontrol Sistemleri II Dersi Grup Adı: Sıvı Seviye Kontrol Deneyi.../../2015 KP Pompa akış sabiti 3.3 cm3/s/v DO1 Çıkış-1 in ağız çapı 0.635 cm DO2
Ege Üniversitesi Elektrik Elektronik Mühendisliği Bölümü Kontrol Sistemleri II Dersi Grup Adı: Sıvı Seviye Kontrol Deneyi.../../2015 KP Pompa akış sabiti 3.3 cm3/s/v DO1 Çıkış-1 in ağız çapı 0.635 cm DO2
Unlike analytical solutions, numerical methods have an error range. In addition to this
 ERROR Unlike analytical solutions, numerical methods have an error range. In addition to this input data may have errors. There are 5 basis source of error: The Source of Error 1. Measuring Errors Data
ERROR Unlike analytical solutions, numerical methods have an error range. In addition to this input data may have errors. There are 5 basis source of error: The Source of Error 1. Measuring Errors Data
A UNIFIED APPROACH IN GPS ACCURACY DETERMINATION STUDIES
 A UNIFIED APPROACH IN GPS ACCURACY DETERMINATION STUDIES by Didem Öztürk B.S., Geodesy and Photogrammetry Department Yildiz Technical University, 2005 Submitted to the Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake
A UNIFIED APPROACH IN GPS ACCURACY DETERMINATION STUDIES by Didem Öztürk B.S., Geodesy and Photogrammetry Department Yildiz Technical University, 2005 Submitted to the Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake
NANO KURġUN ÜRETĠMĠ VE KARAKTERĠZASYONU
 NANO KURġUN ÜRETĠMĠ VE KARAKTERĠZASYONU AHMET GÜNGÖR MERSĠN ÜNĠVERSĠTESĠ FEN BĠLĠMLERĠ ENSTĠTÜSÜ KĠMYA MÜHENDĠSLĠĞĠ ANA BĠLĠM DALI YÜKSEK LĠSANS TEZĠ MERSĠN TEMMUZ 2015 NANO KURġUN ÜRETĠMĠ VE KARAKTERĠZASYONU
NANO KURġUN ÜRETĠMĠ VE KARAKTERĠZASYONU AHMET GÜNGÖR MERSĠN ÜNĠVERSĠTESĠ FEN BĠLĠMLERĠ ENSTĠTÜSÜ KĠMYA MÜHENDĠSLĠĞĠ ANA BĠLĠM DALI YÜKSEK LĠSANS TEZĠ MERSĠN TEMMUZ 2015 NANO KURġUN ÜRETĠMĠ VE KARAKTERĠZASYONU
T.C. SÜLEYMAN DEMİREL ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ ISPARTA İLİ KİRAZ İHRACATININ ANALİZİ
 T.C. SÜLEYMAN DEMİREL ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ ISPARTA İLİ KİRAZ İHRACATININ ANALİZİ Danışman Doç. Dr. Tufan BAL YÜKSEK LİSANS TEZİ TARIM EKONOMİSİ ANABİLİM DALI ISPARTA - 2016 2016 [] TEZ
T.C. SÜLEYMAN DEMİREL ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ ISPARTA İLİ KİRAZ İHRACATININ ANALİZİ Danışman Doç. Dr. Tufan BAL YÜKSEK LİSANS TEZİ TARIM EKONOMİSİ ANABİLİM DALI ISPARTA - 2016 2016 [] TEZ
First Stage of an Automated Content-Based Citation Analysis Study: Detection of Citation Sentences
 First Stage of an Automated Content-Based Citation Analysis Study: Detection of Citation Sentences Zehra Taşkın, Umut Al & Umut Sezen {ztaskin, umutal, u.sezen}@hacettepe.edu.tr - 1 Plan Need for content-based
First Stage of an Automated Content-Based Citation Analysis Study: Detection of Citation Sentences Zehra Taşkın, Umut Al & Umut Sezen {ztaskin, umutal, u.sezen}@hacettepe.edu.tr - 1 Plan Need for content-based
BOĞAZİÇİ UNIVERSITY KANDİLLİ OBSERVATORY and EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH INSTITUTE GEOMAGNETISM LABORATORY
 Monthly Magnetic Bulletin May 2015 BOĞAZİÇİ UNIVERSITY KANDİLLİ OBSERVATORY and EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH INSTITUTE GEOMAGNETISM LABORATORY http://www.koeri.boun.edu.tr/jeomanyetizma/ Magnetic Results from İznik
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin May 2015 BOĞAZİÇİ UNIVERSITY KANDİLLİ OBSERVATORY and EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH INSTITUTE GEOMAGNETISM LABORATORY http://www.koeri.boun.edu.tr/jeomanyetizma/ Magnetic Results from İznik
EGE UNIVERSITY ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING COMMUNICATION SYSTEM LABORATORY
 EGE UNIVERSITY ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING COMMUNICATION SYSTEM LABORATORY INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM EXPERIMENT 4: AMPLITUDE MODULATION Objectives Definition and modulating of Amplitude
EGE UNIVERSITY ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING COMMUNICATION SYSTEM LABORATORY INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM EXPERIMENT 4: AMPLITUDE MODULATION Objectives Definition and modulating of Amplitude
HAZIRLAYANLAR: K. ALBAYRAK, E. CİĞEROĞLU, M. İ. GÖKLER
 HAZIRLAYANLAR: K. ALBAYRAK, E. CİĞEROĞLU, M. İ. GÖKLER PROGRAM OUTCOME 13 Ability to Take Societal, Environmental and Economical Considerations into Account in Professional Activities Program outcome 13
HAZIRLAYANLAR: K. ALBAYRAK, E. CİĞEROĞLU, M. İ. GÖKLER PROGRAM OUTCOME 13 Ability to Take Societal, Environmental and Economical Considerations into Account in Professional Activities Program outcome 13
Darbeli Kırıcılar Impact Crushers
 Darbeli Kırıcılar Impact Crushers TK15-TK16 Serisi Darbeli Kırıcılar TK15-TK16 Series Impact Crushers TK15 ve TK16 darbeli kırıcılar, tesiste sekonder veya tersiyer olarak kullanılabilir özellikte kırıcılardır.
Darbeli Kırıcılar Impact Crushers TK15-TK16 Serisi Darbeli Kırıcılar TK15-TK16 Series Impact Crushers TK15 ve TK16 darbeli kırıcılar, tesiste sekonder veya tersiyer olarak kullanılabilir özellikte kırıcılardır.
PCC 6505 PROFILE CUTTING LINE
 PCC 6505 PROFILE CUTTING LINE 1.DESCRIPTION PCC 6505 is a servo controlled machine which is specifically designed for the serial cutting of any kind of PVC and aluminum s in the market. The machine is
PCC 6505 PROFILE CUTTING LINE 1.DESCRIPTION PCC 6505 is a servo controlled machine which is specifically designed for the serial cutting of any kind of PVC and aluminum s in the market. The machine is
MM103 E COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DRAWING I
 MM103 E COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DRAWING I ORTHOGRAPHIC (MULTIVIEW) PROJECTION (EŞLENİK DİK İZDÜŞÜM) Weeks: 3-6 ORTHOGRAPHIC (MULTIVIEW) PROJECTION (EŞLENİK DİK İZDÜŞÜM) Projection: A view of an object
MM103 E COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DRAWING I ORTHOGRAPHIC (MULTIVIEW) PROJECTION (EŞLENİK DİK İZDÜŞÜM) Weeks: 3-6 ORTHOGRAPHIC (MULTIVIEW) PROJECTION (EŞLENİK DİK İZDÜŞÜM) Projection: A view of an object
WEEK 4 BLM323 NUMERIC ANALYSIS. Okt. Yasin ORTAKCI.
 WEEK 4 BLM33 NUMERIC ANALYSIS Okt. Yasin ORTAKCI yasinortakci@karabuk.edu.tr Karabük Üniversitesi Uzaktan Eğitim Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi BLM33 NONLINEAR EQUATION SYSTEM Two or more degree polinomial
WEEK 4 BLM33 NUMERIC ANALYSIS Okt. Yasin ORTAKCI yasinortakci@karabuk.edu.tr Karabük Üniversitesi Uzaktan Eğitim Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi BLM33 NONLINEAR EQUATION SYSTEM Two or more degree polinomial
4. HAFTA BLM323 SAYISAL ANALİZ. Okt. Yasin ORTAKCI.
 4. HAFTA BLM33 SAYISAL ANALİZ Okt. Yasin ORTAKCI yasinortakci@karabuk.edu.tr Karabük Üniversitesi Uzaktan Eğitim Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi BLM33 NONLINEAR EQUATION SYSTEM Two or more degree polinomial
4. HAFTA BLM33 SAYISAL ANALİZ Okt. Yasin ORTAKCI yasinortakci@karabuk.edu.tr Karabük Üniversitesi Uzaktan Eğitim Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi BLM33 NONLINEAR EQUATION SYSTEM Two or more degree polinomial
Cevher Zenginleştirme, Ar-Ge ve Analiz Hizmetleri Mineral Processing, R&D And Analysis Services XRF - XRD
 Cevher Zenginleştirme, Ar-Ge ve Analiz Hizmetleri Mineral Processing, R&D And Analysis Services XRF - XRD w w w. a r g e t e s t. c o m İçindekiler / Table of Contents XRF-WR - Tam Kayaç Analizi / Whole
Cevher Zenginleştirme, Ar-Ge ve Analiz Hizmetleri Mineral Processing, R&D And Analysis Services XRF - XRD w w w. a r g e t e s t. c o m İçindekiler / Table of Contents XRF-WR - Tam Kayaç Analizi / Whole
24kV,630A Outdoor Switch Disconnector with Arc Quenching Chamber (ELBI) IEC IEC IEC 60129
 24kV,630 Outdoor Switch Disconnector with rc Quenching Chamber (ELBI) IEC265-1 IEC 694 IEC 129 Type ELBI-HN (24kV,630,normal) Closed view Open view Type ELBI-HS (24kV,630,with fuse base) Closed view Open
24kV,630 Outdoor Switch Disconnector with rc Quenching Chamber (ELBI) IEC265-1 IEC 694 IEC 129 Type ELBI-HN (24kV,630,normal) Closed view Open view Type ELBI-HS (24kV,630,with fuse base) Closed view Open
ÇİNKO KATKILI ANTİBAKTERİYEL ÖZELLİKTE HİDROKSİAPATİT ÜRETİMİ VE KARAKTERİZASYONU
 ÇİNKO KATKILI ANTİBAKTERİYEL ÖZELLİKTE HİDROKSİAPATİT ÜRETİMİ VE KARAKTERİZASYONU SÜLEYMAN ÇINAR ÇAĞAN MERSİN ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ MAKİNE MÜHENDİSLİĞİ ANA BİLİM DALI YÜKSEK LİSANS TEZİ
ÇİNKO KATKILI ANTİBAKTERİYEL ÖZELLİKTE HİDROKSİAPATİT ÜRETİMİ VE KARAKTERİZASYONU SÜLEYMAN ÇINAR ÇAĞAN MERSİN ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ MAKİNE MÜHENDİSLİĞİ ANA BİLİM DALI YÜKSEK LİSANS TEZİ
Konsantre Cevher Analizleri / Ore Grade Analysis
 Konsantre Cevher Analizleri / Ore Grade Analysis Bu analiz grupları yüksek tenörlü cevher analizleri için uygun metottur. This analysis groups is an appropriate method for high grade ore analyses. AT-11
Konsantre Cevher Analizleri / Ore Grade Analysis Bu analiz grupları yüksek tenörlü cevher analizleri için uygun metottur. This analysis groups is an appropriate method for high grade ore analyses. AT-11
YARASA VE ÇİFTLİK GÜBRESİNİN BAZI TOPRAK ÖZELLİKLERİ ve BUĞDAY BİTKİSİNİN VERİM PARAMETRELERİ ÜZERİNE ETKİSİ
 ATATÜRK ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ DOKTORA TEZİ YARASA VE ÇİFTLİK GÜBRESİNİN BAZI TOPRAK ÖZELLİKLERİ ve BUĞDAY BİTKİSİNİN VERİM PARAMETRELERİ ÜZERİNE ETKİSİ TARIMSAL YAPILAR VE SULAMA ANABİLİM
ATATÜRK ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ DOKTORA TEZİ YARASA VE ÇİFTLİK GÜBRESİNİN BAZI TOPRAK ÖZELLİKLERİ ve BUĞDAY BİTKİSİNİN VERİM PARAMETRELERİ ÜZERİNE ETKİSİ TARIMSAL YAPILAR VE SULAMA ANABİLİM
ÇEVRESEL TEST HİZMETLERİ 2.ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS
 ÇEVRESEL TEST HİZMETLERİ 2.ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS Çevresel testler askeri ve sivil amaçlı kullanılan alt sistem ve sistemlerin ömür devirleri boyunca karşı karşıya kalabilecekleri doğal çevre şartlarına dirençlerini
ÇEVRESEL TEST HİZMETLERİ 2.ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS Çevresel testler askeri ve sivil amaçlı kullanılan alt sistem ve sistemlerin ömür devirleri boyunca karşı karşıya kalabilecekleri doğal çevre şartlarına dirençlerini
İYC MADENCİLİK SAN. VE TİC. LTD. ŞTİ. NE AİT MUĞLA - FETHİYE YÖRESİ BEJ TÜRÜ KİREÇTAŞININ FİZİKO-MEKANİK ANALİZ RAPORU
 T.C. PAMUKKALE ÜNİVERSİTESİ MÜHENDİSLİK FAKÜLTESİ PAMUKKALE UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING İYC MADENCİLİK SAN. VE TİC. LTD. ŞTİ. NE AİT MUĞLA - FETHİYE YÖRESİ BEJ TÜRÜ KİREÇTAŞININ FİZİKO-MEKANİK ANALİZ
T.C. PAMUKKALE ÜNİVERSİTESİ MÜHENDİSLİK FAKÜLTESİ PAMUKKALE UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING İYC MADENCİLİK SAN. VE TİC. LTD. ŞTİ. NE AİT MUĞLA - FETHİYE YÖRESİ BEJ TÜRÜ KİREÇTAŞININ FİZİKO-MEKANİK ANALİZ
Teşekkür. BOĞAZİÇİ UNIVERSITY KANDİLLİ OBSERVATORY and EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH INSTITUTE GEOMAGNETISM LABORATORY
 Monthly Magnetic Bulletin October 2015 BOĞAZİÇİ UNIVERSITY KANDİLLİ OBSERVATORY and EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH INSTITUTE GEOMAGNETISM LABORATORY http://www.koeri.boun.edu.tr/jeomanyetizma/ Magnetic Results from
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin October 2015 BOĞAZİÇİ UNIVERSITY KANDİLLİ OBSERVATORY and EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH INSTITUTE GEOMAGNETISM LABORATORY http://www.koeri.boun.edu.tr/jeomanyetizma/ Magnetic Results from
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi, Maden Mühendisliği ve Bergama Meslek Yüksekokulu Buca/İzmir/Türkiye
 Yerbilimleri, 2016, 37 (1), 19-26 Hacettepe Üniversitesi Yerbilimleri Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi Bülteni Bulletin of the Earth Sciences Application and Research Centre of Hacettepe University Patlatma
Yerbilimleri, 2016, 37 (1), 19-26 Hacettepe Üniversitesi Yerbilimleri Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi Bülteni Bulletin of the Earth Sciences Application and Research Centre of Hacettepe University Patlatma
Arch Dams. Prof. Dr. Recep YURTAL (Ç.Ü.) Translated from the slides of. by his kind courtesy. ercan kahya
 Arch Dams Translated from the slides of Prof. Dr. (Ç.Ü.) by his kind courtesy ercan kahya Ç.Ü. İnş.Müh.Böl. Arch Dams Curved in plan and carry most of the water thrust horizontally to the side abutments
Arch Dams Translated from the slides of Prof. Dr. (Ç.Ü.) by his kind courtesy ercan kahya Ç.Ü. İnş.Müh.Böl. Arch Dams Curved in plan and carry most of the water thrust horizontally to the side abutments
Performans Tabloları Yalınkat Camlar
 Performans Tabloları Yalınkat Camlar Kaplamalı Yüzey Gün Işığı Soğurma Güneş Enerjisi Direkt Toplam Gölgeleme Isı (U Değeri) W/m 2 K Gümüş #1 38 33 27 30 43 50 0,57 5,7 #2 38 27 20 38 43 52 0,59 5,7 Yeşil
Performans Tabloları Yalınkat Camlar Kaplamalı Yüzey Gün Işığı Soğurma Güneş Enerjisi Direkt Toplam Gölgeleme Isı (U Değeri) W/m 2 K Gümüş #1 38 33 27 30 43 50 0,57 5,7 #2 38 27 20 38 43 52 0,59 5,7 Yeşil
Tekirdağ&Ziraat&Fakültesi&Dergisi&
 NamıkKemalÜniversitesi ISSN:1302*7050 TekirdağZiraatFakültesiDergisi JournalofTekirdagAgriculturalFaculty AnInternationalJournalofallSubjectsofAgriculture Cilt/Volume:11Sayı/Number:1Yıl/Year:2014 Sahibi/Owner
NamıkKemalÜniversitesi ISSN:1302*7050 TekirdağZiraatFakültesiDergisi JournalofTekirdagAgriculturalFaculty AnInternationalJournalofallSubjectsofAgriculture Cilt/Volume:11Sayı/Number:1Yıl/Year:2014 Sahibi/Owner
ISSN: Yıl /Year: 2017 Cilt(Sayı)/Vol.(Issue): 1(Özel) Sayfa/Page: Araştırma Makalesi Research Article. Özet.
 VII. Bahçe Ürünlerinde Muhafaza ve Pazarlama Sempozyumu, 04-07 Ekim 206 ISSN: 248-0036 Yıl /Year: 207 Cilt(Sayı)/Vol.(Issue): (Özel) Sayfa/Page: 54-60 Araştırma Makalesi Research Article Suleyman Demirel
VII. Bahçe Ürünlerinde Muhafaza ve Pazarlama Sempozyumu, 04-07 Ekim 206 ISSN: 248-0036 Yıl /Year: 207 Cilt(Sayı)/Vol.(Issue): (Özel) Sayfa/Page: 54-60 Araştırma Makalesi Research Article Suleyman Demirel
Mukavemet. Betonarme Yapılar. İç Kuvvet Diyagramları. Dr. Haluk Sesigür İ.T.Ü. Mimarlık Fakültesi Yapı ve Deprem Mühendisliği
 Betonarme Yapılar Dr. Haluk Sesigür İ.T.Ü. Mimarlık Fakültesi Yapı ve Deprem Mühendisliği KİRİŞ MESNETLENME TİPLERİ VE YÜKLER KİRİŞ MESNETLENME TİPLERİ VE YÜKLER (a) Basit kiriş (b) Sürekli kiriş (c) Konsol
Betonarme Yapılar Dr. Haluk Sesigür İ.T.Ü. Mimarlık Fakültesi Yapı ve Deprem Mühendisliği KİRİŞ MESNETLENME TİPLERİ VE YÜKLER KİRİŞ MESNETLENME TİPLERİ VE YÜKLER (a) Basit kiriş (b) Sürekli kiriş (c) Konsol
T.C. İSTANBUL AYDIN ÜNİVERSİTESİ SOSYAL BİLİMLER ENSTİTÜSÜ BİREYSEL DEĞERLER İLE GİRİŞİMCİLİK EĞİLİMİ İLİŞKİSİ: İSTANBUL İLİNDE BİR ARAŞTIRMA
 T.C. İSTANBUL AYDIN ÜNİVERSİTESİ SOSYAL BİLİMLER ENSTİTÜSÜ BİREYSEL DEĞERLER İLE GİRİŞİMCİLİK EĞİLİMİ İLİŞKİSİ: İSTANBUL İLİNDE BİR ARAŞTIRMA DOKTORA TEZİ Cafer Şafak EYEL İşletme Ana Bilim Dalı İşletme
T.C. İSTANBUL AYDIN ÜNİVERSİTESİ SOSYAL BİLİMLER ENSTİTÜSÜ BİREYSEL DEĞERLER İLE GİRİŞİMCİLİK EĞİLİMİ İLİŞKİSİ: İSTANBUL İLİNDE BİR ARAŞTIRMA DOKTORA TEZİ Cafer Şafak EYEL İşletme Ana Bilim Dalı İşletme
Marble / Granite / Concrete / Asphalt
 Marble / Granite / Concrete / Asphalt Circular Saws, Diamond Wires, Gang-Saw Blades, Calibrators, Profiles, Custom Made Products Perfect solutions to endless needs... HAKKIMIZDA SONMAK 1975 senesinde Ankara
Marble / Granite / Concrete / Asphalt Circular Saws, Diamond Wires, Gang-Saw Blades, Calibrators, Profiles, Custom Made Products Perfect solutions to endless needs... HAKKIMIZDA SONMAK 1975 senesinde Ankara
6. Seçilmiş 24 erkek tipte ağacın büyüme biçimi, ağacın büyüme gücü (cm), çiçeklenmenin çakışma süresi, bir salkımdaki çiçek tozu üretim miktarı,
 ÖZET Bu çalışmada, Ceylanpınar Tarım İşletmesi'nde bulunan antepfıstığı parsellerinde yer alan bazı erkek tiplerin morfolojik ve biyolojik özelikleri araştırılmıştır. Çalışma, 1995 ve 1996 yıllarında hem
ÖZET Bu çalışmada, Ceylanpınar Tarım İşletmesi'nde bulunan antepfıstığı parsellerinde yer alan bazı erkek tiplerin morfolojik ve biyolojik özelikleri araştırılmıştır. Çalışma, 1995 ve 1996 yıllarında hem
1 I S L U Y G U L A M A L I İ K T İ S A T _ U Y G U L A M A ( 5 ) _ 3 0 K a s ı m
 1 I S L 8 0 5 U Y G U L A M A L I İ K T İ S A T _ U Y G U L A M A ( 5 ) _ 3 0 K a s ı m 2 0 1 2 CEVAPLAR 1. Tekelci bir firmanın sabit bir ortalama ve marjinal maliyet ( = =$5) ile ürettiğini ve =53 şeklinde
1 I S L 8 0 5 U Y G U L A M A L I İ K T İ S A T _ U Y G U L A M A ( 5 ) _ 3 0 K a s ı m 2 0 1 2 CEVAPLAR 1. Tekelci bir firmanın sabit bir ortalama ve marjinal maliyet ( = =$5) ile ürettiğini ve =53 şeklinde
THE IMPACT OF AUTONOMOUS LEARNING ON GRADUATE STUDENTS PROFICIENCY LEVEL IN FOREIGN LANGUAGE LEARNING ABSTRACT
 THE IMPACT OF AUTONOMOUS LEARNING ON GRADUATE STUDENTS PROFICIENCY LEVEL IN FOREIGN LANGUAGE LEARNING ABSTRACT The purpose of the study is to investigate the impact of autonomous learning on graduate students
THE IMPACT OF AUTONOMOUS LEARNING ON GRADUATE STUDENTS PROFICIENCY LEVEL IN FOREIGN LANGUAGE LEARNING ABSTRACT The purpose of the study is to investigate the impact of autonomous learning on graduate students
: Shower Unit (Flat) : Kompakt Duș Ünitesi (Flat)
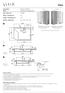 Veo Description Tanım : Shower Unit (Flat) : Kompakt Duș Ünitesi (Flat) Left/Sol Right/Sağ Size / Ebat (cm) : 190x90 Depth / Derinlik (cm) : 3,5 Height / Yükseklik (cm) : 215 Weight / Ağırlık (kg) : min.
Veo Description Tanım : Shower Unit (Flat) : Kompakt Duș Ünitesi (Flat) Left/Sol Right/Sağ Size / Ebat (cm) : 190x90 Depth / Derinlik (cm) : 3,5 Height / Yükseklik (cm) : 215 Weight / Ağırlık (kg) : min.
10.7442 g Na2HPO4.12H2O alınır, 500mL lik balonjojede hacim tamamlanır.
 1-0,12 N 500 ml Na2HPO4 çözeltisi, Na2HPO4.12H2O kullanılarak nasıl hazırlanır? Bu çözeltiden alınan 1 ml lik bir kısım saf su ile 1000 ml ye seyreltiliyor. Son çözelti kaç Normaldir? Kaç ppm dir? % kaçlıktır?
1-0,12 N 500 ml Na2HPO4 çözeltisi, Na2HPO4.12H2O kullanılarak nasıl hazırlanır? Bu çözeltiden alınan 1 ml lik bir kısım saf su ile 1000 ml ye seyreltiliyor. Son çözelti kaç Normaldir? Kaç ppm dir? % kaçlıktır?
GEO-Treat 2000 Series / Serisi. GEO-Treat 1000 Series / Serisi RESERVOIR TEMPERATURE HIGHER THAN 180 C RESERVOIR TEMPERATURE BETWEEN 120 C C
 1000 Series / Serisi RESERVOIR TEMPERATURE HIGHER THAN 180 C Scale inhibitors showing high performance even at low dosages which are designed for wells with reservoir temperatures higher than 180 C and
1000 Series / Serisi RESERVOIR TEMPERATURE HIGHER THAN 180 C Scale inhibitors showing high performance even at low dosages which are designed for wells with reservoir temperatures higher than 180 C and
GEO-Treat 2000 Series / Serisi. GEO-Treat 1000 Series / Serisi RESERVOIR TEMPERATURE HIGHER THAN 180 C RESERVOIR TEMPERATURE BETWEEN 120 C C
 1000 Series / Serisi RESERVOIR TEMPERATURE HIGHER THAN 180 C Scale inhibitors showing high performance even at low dosages which are designed for wells with reservoir temperatures higher than 180 C and
1000 Series / Serisi RESERVOIR TEMPERATURE HIGHER THAN 180 C Scale inhibitors showing high performance even at low dosages which are designed for wells with reservoir temperatures higher than 180 C and
Eco 338 Economic Policy Week 4 Fiscal Policy- I. Prof. Dr. Murat Yulek Istanbul Ticaret University
 Eco 338 Economic Policy Week 4 Fiscal Policy- I Prof. Dr. Murat Yulek Istanbul Ticaret University Aggregate Demand Aggregate (domestic) demand (or domestic absorption) is the sum of consumption, investment
Eco 338 Economic Policy Week 4 Fiscal Policy- I Prof. Dr. Murat Yulek Istanbul Ticaret University Aggregate Demand Aggregate (domestic) demand (or domestic absorption) is the sum of consumption, investment
Jeokimya Analizleri. Geochemical Analysis
 Jeokimya Analizleri Geochemical Analysis Jeokimya; minerallerin oluşumu esnasında ve sonrasında çevre kayaçlar ile yüzeysel ortamlarda gerçekleşen kimyasal değişikliklerin belirlenmesi temeline dayanır.
Jeokimya Analizleri Geochemical Analysis Jeokimya; minerallerin oluşumu esnasında ve sonrasında çevre kayaçlar ile yüzeysel ortamlarda gerçekleşen kimyasal değişikliklerin belirlenmesi temeline dayanır.
Araziye Çıkmadan Önce Mutlaka Bizi Arayınız!
 Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March 2014 z BOĞAZİÇİ UNIVERSITY KANDİLLİ OBSERVATORY and EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH INSTITUTE GEOMAGNETISM LABORATORY http://www.koeri.boun.edu.tr/jeofizik/default.htm Magnetic Results
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin March 2014 z BOĞAZİÇİ UNIVERSITY KANDİLLİ OBSERVATORY and EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH INSTITUTE GEOMAGNETISM LABORATORY http://www.koeri.boun.edu.tr/jeofizik/default.htm Magnetic Results
ISSN: Yıl /Year: 2017 Cilt(Sayı)/Vol.(Issue): 1(Özel) Sayfa/Page: Araştırma Makalesi Research Article
 VII. Bahçe Ürünlerinde Muhafaza ve Pazarlama Sempozyumu, 04-07 Ekim 2016 1 Incir ISSN: 2148-0036 Yıl /Year: 2017 Cilt(Sayı)/Vol.(Issue): 1(Özel) Sayfa/Page: 15-23 Araştırma Makalesi Research Article Araştırma
VII. Bahçe Ürünlerinde Muhafaza ve Pazarlama Sempozyumu, 04-07 Ekim 2016 1 Incir ISSN: 2148-0036 Yıl /Year: 2017 Cilt(Sayı)/Vol.(Issue): 1(Özel) Sayfa/Page: 15-23 Araştırma Makalesi Research Article Araştırma
İŞLETMELERDE KURUMSAL İMAJ VE OLUŞUMUNDAKİ ANA ETKENLER
 ANKARA ÜNİVERSİTESİ SOSYAL BİLİMLER ENSTİTÜSÜ HALKLA İLİŞKİLER VE TANITIM ANA BİLİM DALI İŞLETMELERDE KURUMSAL İMAJ VE OLUŞUMUNDAKİ ANA ETKENLER BİR ÖRNEK OLAY İNCELEMESİ: SHERATON ANKARA HOTEL & TOWERS
ANKARA ÜNİVERSİTESİ SOSYAL BİLİMLER ENSTİTÜSÜ HALKLA İLİŞKİLER VE TANITIM ANA BİLİM DALI İŞLETMELERDE KURUMSAL İMAJ VE OLUŞUMUNDAKİ ANA ETKENLER BİR ÖRNEK OLAY İNCELEMESİ: SHERATON ANKARA HOTEL & TOWERS
Gelir Dağılımı ve Yoksulluk
 19 Decembre 2014 Gini-coefficient of inequality: This is the most commonly used measure of inequality. The coefficient varies between 0, which reflects complete equality and 1, which indicates complete
19 Decembre 2014 Gini-coefficient of inequality: This is the most commonly used measure of inequality. The coefficient varies between 0, which reflects complete equality and 1, which indicates complete
C5 Mugla White
 Sayfa 1/8 Page 1/8 Müşterinin Adı/Adresi: Customer Name/Adress: Raport No: Report No: ÇOBANLAR MERMER MADENCİLİK TURZ. TİC. VE İNŞ. A.Ş. Salkım Mah. Çıngıl Sok. No:7 Kavaklıdere/MUĞLA 227 Numunenin Adı
Sayfa 1/8 Page 1/8 Müşterinin Adı/Adresi: Customer Name/Adress: Raport No: Report No: ÇOBANLAR MERMER MADENCİLİK TURZ. TİC. VE İNŞ. A.Ş. Salkım Mah. Çıngıl Sok. No:7 Kavaklıdere/MUĞLA 227 Numunenin Adı
Calacatta Oro
 Sayfa 1/8 Page 1/8 Müşterinin Adı/Adresi: Customer Name/Adress: Raport No: Report No: KOMMERSAN KOMBASSAN MERMER MADEN İŞLETMELERİ SAN VE TİC. A.Ş Muğla Aydın Karayolu 12. Km Salih Paşalar Mevkii Bayır
Sayfa 1/8 Page 1/8 Müşterinin Adı/Adresi: Customer Name/Adress: Raport No: Report No: KOMMERSAN KOMBASSAN MERMER MADEN İŞLETMELERİ SAN VE TİC. A.Ş Muğla Aydın Karayolu 12. Km Salih Paşalar Mevkii Bayır
Dersin Kodu Dersin Adı Dersin Türü Yıl Yarıyıl AKTS 507004092007 MAKİNA PROJESİ II Zorunlu 4 7 4
 Ders Öğretim Planı Dersin Kodu Dersin Adı Dersin Türü Yıl Yarıyıl AKTS 507004092007 MAKİNA PROJESİ II Zorunlu 4 7 4 Dersin Seviyesi Lisans Dersin Amacı Dersin amacı Makina Mühendisliği bölümü Lisans öğrencilerine
Ders Öğretim Planı Dersin Kodu Dersin Adı Dersin Türü Yıl Yarıyıl AKTS 507004092007 MAKİNA PROJESİ II Zorunlu 4 7 4 Dersin Seviyesi Lisans Dersin Amacı Dersin amacı Makina Mühendisliği bölümü Lisans öğrencilerine
DOKUZ EYLUL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING OFFICE OF THE DEAN COURSE / MODULE / BLOCK DETAILS ACADEMIC YEAR / SEMESTER. Course Code: MAK 2029
 Offered by: Makina Mühendisliği Course Title: STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Course Org. Title: MUKAVEMET Course Level: Lisans Course Code: MAK 09 Language of Instruction: Türkçe Form Submitting/Renewal Date 18/09/01
Offered by: Makina Mühendisliği Course Title: STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Course Org. Title: MUKAVEMET Course Level: Lisans Course Code: MAK 09 Language of Instruction: Türkçe Form Submitting/Renewal Date 18/09/01
BBM Discrete Structures: Final Exam Date: , Time: 15:00-17:00
 BBM 205 - Discrete Structures: Final Exam Date: 12.1.2017, Time: 15:00-17:00 Ad Soyad / Name: Ögrenci No /Student ID: Question: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Total Points: 6 16 8 8 10 9 6 8 14 5 10 100 Score:
BBM 205 - Discrete Structures: Final Exam Date: 12.1.2017, Time: 15:00-17:00 Ad Soyad / Name: Ögrenci No /Student ID: Question: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Total Points: 6 16 8 8 10 9 6 8 14 5 10 100 Score:
UBE Machine Learning. Kaya Oguz
 UBE 521 - Machine Learning Kaya Oguz Support Vector Machines How to divide up the space with decision boundaries? 1990s - new compared to other methods. How to make the decision rule to use with this boundary?
UBE 521 - Machine Learning Kaya Oguz Support Vector Machines How to divide up the space with decision boundaries? 1990s - new compared to other methods. How to make the decision rule to use with this boundary?
İZDÜŞÜM. İzdüşümün Tanımı ve Önemi İzdüşüm Metodları Temel İzdüşüm Düzlemleri Noktanın İzdüşümü Doğrunun İzdüşümü Düzlemlerin İz Düşümleri
 ÖĞR. GÖR.ÖMER UÇTU İZDÜŞÜM İzdüşümün Tanımı ve Önemi İzdüşüm Metodları Temel İzdüşüm Düzlemleri Noktanın İzdüşümü Doğrunun İzdüşümü Düzlemlerin İz Düşümleri İzdüşümün Tanımı ve Önemi İz düşüm: Bir cismin
ÖĞR. GÖR.ÖMER UÇTU İZDÜŞÜM İzdüşümün Tanımı ve Önemi İzdüşüm Metodları Temel İzdüşüm Düzlemleri Noktanın İzdüşümü Doğrunun İzdüşümü Düzlemlerin İz Düşümleri İzdüşümün Tanımı ve Önemi İz düşüm: Bir cismin
FUR-FUS çerçeve montaj dübeli
 Uyarlanabilir çoklu altlıklı dübel VERSIYONLAR ONAYLAR galvanize çelik paslanmaz çelik YAPI MALZEMELERI Beton C12/15 Düşey delikli tuğla Delikli kum-kireç tuğla Sağlam kum-kireç tuğla Hafif betondan yapılmış
Uyarlanabilir çoklu altlıklı dübel VERSIYONLAR ONAYLAR galvanize çelik paslanmaz çelik YAPI MALZEMELERI Beton C12/15 Düşey delikli tuğla Delikli kum-kireç tuğla Sağlam kum-kireç tuğla Hafif betondan yapılmış
Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks
 Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks Metamorphic rocks (from the Greek meta, change and morpho, shape ) constitute the third major group of rocks. They result from the transformation of other rocks by metamorphic
Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks Metamorphic rocks (from the Greek meta, change and morpho, shape ) constitute the third major group of rocks. They result from the transformation of other rocks by metamorphic
KOCAELİ ÜNİVERSİTESİ Ford Otosan İhsaniye Otomotiv MYO
 KOCAELİ ÜNİVERSİTESİ Ford Otosan İhsaniye Otomotiv MYO Yüzey İşlemleri Ar-Ge Laboratuarı Yıllık Rapor/ 2014 2 Ġçindekiler Giriş Alt Yapı Çalışmaları Çalışma Grupları Yürütülen/Tamamlanan Projeler Yürütülen/
KOCAELİ ÜNİVERSİTESİ Ford Otosan İhsaniye Otomotiv MYO Yüzey İşlemleri Ar-Ge Laboratuarı Yıllık Rapor/ 2014 2 Ġçindekiler Giriş Alt Yapı Çalışmaları Çalışma Grupları Yürütülen/Tamamlanan Projeler Yürütülen/
AEX METAL MADENCİLİK A.Ş.
 AEX METAL MADENCİLİK A.Ş. 1 2 ÖZET BİLGİ AEX, modern araştırma tekniği yöntemleri ile ALANYA MASİF madencilik bölgesinde yeni ekonomik maden yatakları keşfetmeyi amaçlamaktadır. 1940 lı yıllardan günümüze
AEX METAL MADENCİLİK A.Ş. 1 2 ÖZET BİLGİ AEX, modern araştırma tekniği yöntemleri ile ALANYA MASİF madencilik bölgesinde yeni ekonomik maden yatakları keşfetmeyi amaçlamaktadır. 1940 lı yıllardan günümüze
NOVAPAC Ambalaj San. Tic. A.Ş
 Ambalaj San. Tic. A.Ş 2014 yılında İstanbul'da 5.000 m2 lik alanda kurulan tek kullanımlık plastik ürünleri araştırıp, geliştirip, tasarlayıp üretmektedir. Uzun yılların deneyimi ile pazara yenilikçi,
Ambalaj San. Tic. A.Ş 2014 yılında İstanbul'da 5.000 m2 lik alanda kurulan tek kullanımlık plastik ürünleri araştırıp, geliştirip, tasarlayıp üretmektedir. Uzun yılların deneyimi ile pazara yenilikçi,
ANKARA ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ DÖNEM PROJESİ TAŞINMAZ DEĞERLEMEDE HEDONİK REGRESYON ÇÖZÜMLEMESİ. Duygu ÖZÇALIK
 ANKARA ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ DÖNEM PROJESİ TAŞINMAZ DEĞERLEMEDE HEDONİK REGRESYON ÇÖZÜMLEMESİ Duygu ÖZÇALIK GAYRİMENKUL GELİŞTİRME VE YÖNETİMİ ANABİLİM DALI ANKARA 2018 Her hakkı saklıdır
ANKARA ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ DÖNEM PROJESİ TAŞINMAZ DEĞERLEMEDE HEDONİK REGRESYON ÇÖZÜMLEMESİ Duygu ÖZÇALIK GAYRİMENKUL GELİŞTİRME VE YÖNETİMİ ANABİLİM DALI ANKARA 2018 Her hakkı saklıdır
C6 Mugla White
 Sayfa 1/8 Page 1/8 Müşterinin Adı/Adresi: Customer Name/Adress: Raport No: Report No: ÇOBANLAR MERMER MADENCİLİK TURZ. TİC. VE İNŞ. A.Ş. Salkım Mah. Çıngıl Sok. No:7 Kavaklıdere/MUĞLA 228 Numunenin Adı
Sayfa 1/8 Page 1/8 Müşterinin Adı/Adresi: Customer Name/Adress: Raport No: Report No: ÇOBANLAR MERMER MADENCİLİK TURZ. TİC. VE İNŞ. A.Ş. Salkım Mah. Çıngıl Sok. No:7 Kavaklıdere/MUĞLA 228 Numunenin Adı
DOKUZ EYLUL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING OFFICE OF THE DEAN COURSE / MODULE / BLOCK DETAILS ACADEMIC YEAR / SEMESTER. Course Code: MMM 4027
 Offered by: Metalurji ve Malzeme Mühendisliği Course Title: MATERIALS OF SPACE AND AVIATION Course Org. Title: UZAY VE HAVACILIK MALZEMELERİ Course Level: Lisans Course Code: MMM 027 Language of Instruction:
Offered by: Metalurji ve Malzeme Mühendisliği Course Title: MATERIALS OF SPACE AND AVIATION Course Org. Title: UZAY VE HAVACILIK MALZEMELERİ Course Level: Lisans Course Code: MMM 027 Language of Instruction:
BOĞAZİÇİ UNIVERSITY KANDİLLİ OBSERVATORY and EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH INSTITUTE GEOMAGNETISM LABORATORY
 Monthly Magnetic Bulletin June 2014 BOĞAZİÇİ UNIVERSITY KANDİLLİ OBSERVATORY and EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH INSTITUTE GEOMAGNETISM LABORATORY http://www.koeri.boun.edu.tr/jeomanyetizma/ Magnetic Results from
Monthly Magnetic Bulletin June 2014 BOĞAZİÇİ UNIVERSITY KANDİLLİ OBSERVATORY and EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH INSTITUTE GEOMAGNETISM LABORATORY http://www.koeri.boun.edu.tr/jeomanyetizma/ Magnetic Results from
Arýza Giderme. Troubleshooting
 Arýza Giderme Sorun Olasý Nedenler Giriþ Gerilimi düþük hata mesajý Þebeke giriþ gerilimi alt seviyenin altýnda geliyor Þebeke giriþ gerilimi tehlikeli derecede Yüksek geliyor Regülatör kontrol kartý hatasý
Arýza Giderme Sorun Olasý Nedenler Giriþ Gerilimi düþük hata mesajý Þebeke giriþ gerilimi alt seviyenin altýnda geliyor Þebeke giriþ gerilimi tehlikeli derecede Yüksek geliyor Regülatör kontrol kartý hatasý
ÖZGEÇMİŞ Prof. Dr. TUĞRUL ÜNLÜ
 ÖZGEÇMİŞ Prof. Dr. TUĞRUL ÜNLÜ Doğum Yılı: 1963 Yazışma Adresi: Telefon : 372-2574010/1197 Faks : 372-2574023 e-posta : EĞİTİM BİLGİLERİ Universitesi Mühendislik Fakültesi Bölümü 67100 Zonguldak/Türkiye
ÖZGEÇMİŞ Prof. Dr. TUĞRUL ÜNLÜ Doğum Yılı: 1963 Yazışma Adresi: Telefon : 372-2574010/1197 Faks : 372-2574023 e-posta : EĞİTİM BİLGİLERİ Universitesi Mühendislik Fakültesi Bölümü 67100 Zonguldak/Türkiye
HÜRRİYET GAZETESİ: 1948-1953 DÖNEMİNİN YAYIN POLİTİKASI
 T.C. ANKARA ÜNİVERSİTESİ SOSYAL BİLİMLER ENSTİTÜSÜ GAZETECİLİK ANABİLİM DALI HÜRRİYET GAZETESİ: 1948-1953 DÖNEMİNİN YAYIN POLİTİKASI Doktora Tezi Selda Bulut Tez Danışmanı Prof.Dr.Korkmaz Alemdar Ankara-2007
T.C. ANKARA ÜNİVERSİTESİ SOSYAL BİLİMLER ENSTİTÜSÜ GAZETECİLİK ANABİLİM DALI HÜRRİYET GAZETESİ: 1948-1953 DÖNEMİNİN YAYIN POLİTİKASI Doktora Tezi Selda Bulut Tez Danışmanı Prof.Dr.Korkmaz Alemdar Ankara-2007
Zest. : Shower Unit (Flat) Kompakt Duş Ünitesi (Flat) Description Tan m. : 90x90. Size / Ebat (cm) : 2.5. Depth / Derinlik (cm) Weight / A rl k (kg)
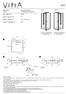 Zest Description Tan m : Shower Unit (Flat) Kompakt Duş Ünitesi (Flat) Left/Sol Right/Sağ Size / Ebat (cm) : 90x90 Depth / Derinlik (cm) : 2.5 Weight / A rl k (kg) : min. 75 max. 90 Height / Yükseklik
Zest Description Tan m : Shower Unit (Flat) Kompakt Duş Ünitesi (Flat) Left/Sol Right/Sağ Size / Ebat (cm) : 90x90 Depth / Derinlik (cm) : 2.5 Weight / A rl k (kg) : min. 75 max. 90 Height / Yükseklik
Doç. Dr. Hakan Cengizler
 Doç. Dr. Hakan Cengizler FOTO ÖĞRENİM DURUMU Derece Üniversite Bölüm / Program Lisans Ege Üniversitesi, Maden Mühendisliği Bölümü 975 Makina Fakültesi 979 Dokuz Eylül Maden Mühendisliği Bölümü 985 Y. Lisans
Doç. Dr. Hakan Cengizler FOTO ÖĞRENİM DURUMU Derece Üniversite Bölüm / Program Lisans Ege Üniversitesi, Maden Mühendisliği Bölümü 975 Makina Fakültesi 979 Dokuz Eylül Maden Mühendisliği Bölümü 985 Y. Lisans
zeytinist
 1 T.C. BALIKESİR ÜNİVERSİTESİ EDREMİT MESLEK YÜKSEKOKULU Zeytincilik ve Zeytin İşleme Teknolojisi Programı Öğr. Gör. Mücahit KIVRAK 0 505 772 44 46 kivrak@gmail.com www.mucahitkivrak.com.tr 2 3 4 TEREYAĞI
1 T.C. BALIKESİR ÜNİVERSİTESİ EDREMİT MESLEK YÜKSEKOKULU Zeytincilik ve Zeytin İşleme Teknolojisi Programı Öğr. Gör. Mücahit KIVRAK 0 505 772 44 46 kivrak@gmail.com www.mucahitkivrak.com.tr 2 3 4 TEREYAĞI
SBR331 Egzersiz Biyomekaniği
 SBR331 Egzersiz Biyomekaniği Açısal Kinematik 1 Angular Kinematics 1 Serdar Arıtan serdar.aritan@hacettepe.edu.tr Mekanik bilimi hareketli bütün cisimlerin hareketlerinin gözlemlenebildiği en asil ve kullanışlı
SBR331 Egzersiz Biyomekaniği Açısal Kinematik 1 Angular Kinematics 1 Serdar Arıtan serdar.aritan@hacettepe.edu.tr Mekanik bilimi hareketli bütün cisimlerin hareketlerinin gözlemlenebildiği en asil ve kullanışlı
MOZAİK SANATI ANTAKYA VE ZEUGMA MOZAİKLERİNİN RESİM ANALİZLERİ MEHMET ŞAHİN. YÜKSEK LİSANS TEZİ Resim Ana Sanat Dalı Danışman: Doç.
 MOZAİK SANATI ANTAKYA VE ZEUGMA MOZAİKLERİNİN RESİM ANALİZLERİ MEHMET ŞAHİN Yüksek Lisans Tezi Eskişehir 2010 MOZAİK SANATI ANTAKYA VE ZEUGMA MOZAİKLERİNİN RESİM ANALİZLERİ MEHMET ŞAHİN YÜKSEK LİSANS TEZİ
MOZAİK SANATI ANTAKYA VE ZEUGMA MOZAİKLERİNİN RESİM ANALİZLERİ MEHMET ŞAHİN Yüksek Lisans Tezi Eskişehir 2010 MOZAİK SANATI ANTAKYA VE ZEUGMA MOZAİKLERİNİN RESİM ANALİZLERİ MEHMET ŞAHİN YÜKSEK LİSANS TEZİ
12. HAFTA BLM323 SAYISAL ANALİZ. Okt. Yasin ORTAKCI. yasinortakci@karabuk.edu.tr
 1. HAFTA BLM33 SAYISAL ANALİZ Okt. Yasin ORTAKCI yasinortakci@karabuk.edu.tr Karabük Üniversitesi Uzaktan Eğitim Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi DIVIDED DIFFERENCE INTERPOLATION Forward Divided Differences
1. HAFTA BLM33 SAYISAL ANALİZ Okt. Yasin ORTAKCI yasinortakci@karabuk.edu.tr Karabük Üniversitesi Uzaktan Eğitim Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi DIVIDED DIFFERENCE INTERPOLATION Forward Divided Differences
C O N T E N T S BHD BHD page 2-5 BHD page 6-9 BHD page BHD page page BHD
 C O N T E N T S BHD 32 + 4 BHD 28 + 4 BHD 24 + 3 page 2-5 page 6-9 BHD 19 + 3 page 10-13 BHD 18 + 3 page 14-17 BHD 18 + 3 page 18-21 BHD 17 + 3 page 18-21 BHDM 12 + 3 page 22-25 page 26-28 Boom Makina;
C O N T E N T S BHD 32 + 4 BHD 28 + 4 BHD 24 + 3 page 2-5 page 6-9 BHD 19 + 3 page 10-13 BHD 18 + 3 page 14-17 BHD 18 + 3 page 18-21 BHD 17 + 3 page 18-21 BHDM 12 + 3 page 22-25 page 26-28 Boom Makina;
Bağlaç 88 adet P. Phrase 6 adet Toplam 94 adet
 ÖNEMLİ BAĞLAÇLAR Bu liste YDS için Önemli özellikle seçilmiş bağlaçları içerir. 88 adet P. Phrase 6 adet Toplam 94 adet Bu doküman, YDS ye hazırlananlar için dinamik olarak oluşturulmuştur. 1. although
ÖNEMLİ BAĞLAÇLAR Bu liste YDS için Önemli özellikle seçilmiş bağlaçları içerir. 88 adet P. Phrase 6 adet Toplam 94 adet Bu doküman, YDS ye hazırlananlar için dinamik olarak oluşturulmuştur. 1. although
TEST RESULTS UFED, XRY and SIMCON
 TEST RESULTS UFED, XRY and SIMCON Test material : SIM card Tested software : UFED 3.6, XRY 6.5, SIMcon v1.2 Expected results : Proper extraction of SMS messages Date of the test : 02.04.2013 Note : The
TEST RESULTS UFED, XRY and SIMCON Test material : SIM card Tested software : UFED 3.6, XRY 6.5, SIMcon v1.2 Expected results : Proper extraction of SMS messages Date of the test : 02.04.2013 Note : The
PRELIMINARY REPORT. 19/09/2012 KAHRAMANMARAŞ PAZARCIK EARTHQUAKE (SOUTHEAST TURKEY) Ml=5.1.
 PRELIMINARY REPORT 19/09/2012 KAHRAMANMARAŞ PAZARCIK EARTHQUAKE (SOUTHEAST TURKEY) Ml=5.1 www.deprem.gov.tr www.afad.gov.tr REPUBLIC OF TUKEY MANAGEMENT PRESIDENCY An earthquake with magnitude Ml=5.1 occurred
PRELIMINARY REPORT 19/09/2012 KAHRAMANMARAŞ PAZARCIK EARTHQUAKE (SOUTHEAST TURKEY) Ml=5.1 www.deprem.gov.tr www.afad.gov.tr REPUBLIC OF TUKEY MANAGEMENT PRESIDENCY An earthquake with magnitude Ml=5.1 occurred
Numune Kodu ve parti no
 Numune Kodu ve parti no Numune tipi Kimin tarafından üretildiği Numune formu ve şekli Sertifikalandıran Kurum Konsantrasyonlar Elde edilen konsantrasyon değerleri Ortalama Standart Sapmalar % 95 Karbon
Numune Kodu ve parti no Numune tipi Kimin tarafından üretildiği Numune formu ve şekli Sertifikalandıran Kurum Konsantrasyonlar Elde edilen konsantrasyon değerleri Ortalama Standart Sapmalar % 95 Karbon
BBM Discrete Structures: Midterm 2 Date: , Time: 16:00-17:30. Question: Total Points: Score:
 BBM 205 - Discrete Structures: Midterm 2 Date: 8.12.2016, Time: 16:00-17:30 Ad Soyad / Name: Ögrenci No /Student ID: Question: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Total Points: 12 22 10 10 15 16 15 100 Score: 1. (12 points)
BBM 205 - Discrete Structures: Midterm 2 Date: 8.12.2016, Time: 16:00-17:30 Ad Soyad / Name: Ögrenci No /Student ID: Question: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Total Points: 12 22 10 10 15 16 15 100 Score: 1. (12 points)
Cases in the Turkish Language
 Fluentinturkish.com Cases in the Turkish Language Grammar Cases Postpositions, circumpositions and prepositions are the words or morphemes that express location to some kind of reference. They are all
Fluentinturkish.com Cases in the Turkish Language Grammar Cases Postpositions, circumpositions and prepositions are the words or morphemes that express location to some kind of reference. They are all
ISO 9001:
 ISO 9001:2015 Aygünsan Demir Çelik 1992 yılında sıcak haddelenmiş ve soğuk çekme olarak üretime başlayan firmamız kaliteyi, teknolojik gelişmeyi ve müşteri memnuniyetini ilke edinerek Karabük ili ve Safranbolu
ISO 9001:2015 Aygünsan Demir Çelik 1992 yılında sıcak haddelenmiş ve soğuk çekme olarak üretime başlayan firmamız kaliteyi, teknolojik gelişmeyi ve müşteri memnuniyetini ilke edinerek Karabük ili ve Safranbolu
HAKKIMIZDA ABOUT US. kuruluşundan bugüne PVC granül sektöründe küresel ve etkin bir oyuncu olmaktır.
 ABOUT US HAKKIMIZDA FORPLAS ın temel amacı, kuruluşundan bugüne PVC granül sektöründe küresel ve etkin bir oyuncu olmaktır. 25 yılı aşkın üretim deneyimine sahip olan FORPLAS, geniş ve nitelikli ürün yelpazesiyle
ABOUT US HAKKIMIZDA FORPLAS ın temel amacı, kuruluşundan bugüne PVC granül sektöründe küresel ve etkin bir oyuncu olmaktır. 25 yılı aşkın üretim deneyimine sahip olan FORPLAS, geniş ve nitelikli ürün yelpazesiyle
Hakkımızda / About Us... Tunç Makina 1980'den günümüze imal ettiği Eksantrik Presler de kullanmış olduğu,kaliteli malzemelerle imalatını uygulayarak,k
 Hakkımızda / About Us... Tunç Makina 1980'den günümüze imal ettiği Eksantrik Presler de kullanmış olduğu,kaliteli malzemelerle imalatını uygulayarak,kendi alanında daima en iyiyi amaç edinmiştir. Kaliteli
Hakkımızda / About Us... Tunç Makina 1980'den günümüze imal ettiği Eksantrik Presler de kullanmış olduğu,kaliteli malzemelerle imalatını uygulayarak,kendi alanında daima en iyiyi amaç edinmiştir. Kaliteli
daha çok göz önünde bulundurulabilir. Öğrencilerin dile karşı daha olumlu bir tutum geliştirmeleri ve daha homojen gruplar ile dersler yürütülebilir.
 ÖZET Üniversite Öğrencilerinin Yabancı Dil Seviyelerinin ve Yabancı Dil Eğitim Programına Karşı Tutumlarının İncelenmesi (Aksaray Üniversitesi Örneği) Çağan YILDIRAN Niğde Üniversitesi, Sosyal Bilimler
ÖZET Üniversite Öğrencilerinin Yabancı Dil Seviyelerinin ve Yabancı Dil Eğitim Programına Karşı Tutumlarının İncelenmesi (Aksaray Üniversitesi Örneği) Çağan YILDIRAN Niğde Üniversitesi, Sosyal Bilimler
DOKUZ EYLUL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING OFFICE OF THE DEAN COURSE / MODULE / BLOCK DETAILS ACADEMIC YEAR / SEMESTER. Course Code: MMM 4039
 Offered by: Metalurji ve Malzeme Mühendisliği Course Title: STRUCTURAL CERAMICS Course Org. Title: YAPI SERAMİKLERİ Course Level: Lisans Course Code: MMM 09 Language of Instruction: Türkçe Form Submitting/Renewal
Offered by: Metalurji ve Malzeme Mühendisliği Course Title: STRUCTURAL CERAMICS Course Org. Title: YAPI SERAMİKLERİ Course Level: Lisans Course Code: MMM 09 Language of Instruction: Türkçe Form Submitting/Renewal
a, ı ı o, u u e, i i ö, ü ü
 Possessive Endings In English, the possession of an object is described by adding an s at the end of the possessor word separated by an apostrophe. If we are talking about a pen belonging to Hakan we would
Possessive Endings In English, the possession of an object is described by adding an s at the end of the possessor word separated by an apostrophe. If we are talking about a pen belonging to Hakan we would
Ad Soyad: Öğrenci No:...
 FİZ 121 2015-2016 Güz Dönemi 2. Vize Sınavı Süre 90 dakikadır 1 2 3 4 5 Toplam Ad Soyad: Öğrenci No:... Sınav sırasında hesap makinası kullanılması serbest, ancak alışverişi yasaktır. Sorular eşit puanlıdır.
FİZ 121 2015-2016 Güz Dönemi 2. Vize Sınavı Süre 90 dakikadır 1 2 3 4 5 Toplam Ad Soyad: Öğrenci No:... Sınav sırasında hesap makinası kullanılması serbest, ancak alışverişi yasaktır. Sorular eşit puanlıdır.
BVCD DÝKDÖRTGEN HAVA DAMPERÝ ( BVCD) RECTANGULAR VOLUME CONTROL DAMPER
 DÝKDÖRTGEN HAVA DAMPERÝ ( ) RECTANGULAR VOLUME CONTROL DAMPER Dikdörtgen Hava Damperi Teknik Detaylarý Rectangular Volume Control Damper Technical Details : Malzeme: Ürün kasa ve kanatlarýnýn tamamý ekstrüzyon
DÝKDÖRTGEN HAVA DAMPERÝ ( ) RECTANGULAR VOLUME CONTROL DAMPER Dikdörtgen Hava Damperi Teknik Detaylarý Rectangular Volume Control Damper Technical Details : Malzeme: Ürün kasa ve kanatlarýnýn tamamý ekstrüzyon
by Karin Şeşetyan BS. In C.E., Boğaziçi University, 1994
 A PROBABILISTIC ASSESSMENT OF THE SEISMIC HAZARD IN THE CAUCASUS IN TERMS OF SPECTRAL VALUES by Karin Şeşetyan BS. In C.E., Boğaziçi University, 1994 Submitted to Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research
A PROBABILISTIC ASSESSMENT OF THE SEISMIC HAZARD IN THE CAUCASUS IN TERMS OF SPECTRAL VALUES by Karin Şeşetyan BS. In C.E., Boğaziçi University, 1994 Submitted to Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research
MAJOR QSB STEEL and APPLICATIONS
 MAJOR QSB STEEL and APPLICATIONS No Steel Group Grade Description Applications 1 4140 Chromium, Molybdenum steel for applications requiring high tensile strength and toughness values, in particular in
MAJOR QSB STEEL and APPLICATIONS No Steel Group Grade Description Applications 1 4140 Chromium, Molybdenum steel for applications requiring high tensile strength and toughness values, in particular in
AKDENİZ ÜNİVERSİTESİ MÜHENDİSLİK FAKÜLTESİ ÇEVRE MÜHENDİSLİĞİ BÖLÜMÜ ÇEV181 TEKNİK İNGİLİZCE I
 AKDENİZ ÜNİVERSİTESİ MÜHENDİSLİK FAKÜLTESİ ÇEVRE MÜHENDİSLİĞİ BÖLÜMÜ ÇEV181 TEKNİK İNGİLİZCE I Dr. Öğr. Üyesi Firdes YENİLMEZ KTS Kredisi 3 (Kurumsal Saat: 2 Uygulama Saat: 1) Ders Programı Pazartesi 09:30-12:20
AKDENİZ ÜNİVERSİTESİ MÜHENDİSLİK FAKÜLTESİ ÇEVRE MÜHENDİSLİĞİ BÖLÜMÜ ÇEV181 TEKNİK İNGİLİZCE I Dr. Öğr. Üyesi Firdes YENİLMEZ KTS Kredisi 3 (Kurumsal Saat: 2 Uygulama Saat: 1) Ders Programı Pazartesi 09:30-12:20
KULLANILAN MADDE TÜRÜNE GÖRE BAĞIMLILIK PROFİLİ DEĞİŞİKLİK GÖSTERİYOR MU? Kültegin Ögel, Figen Karadağ, Cüneyt Evren, Defne Tamar Gürol
 KULLANILAN MADDE TÜRÜNE GÖRE BAĞIMLILIK PROFİLİ DEĞİŞİKLİK GÖSTERİYOR MU? Kültegin Ögel, Figen Karadağ, Cüneyt Evren, Defne Tamar Gürol 1 Acibadem University Medical Faculty 2 Maltepe University Medical
KULLANILAN MADDE TÜRÜNE GÖRE BAĞIMLILIK PROFİLİ DEĞİŞİKLİK GÖSTERİYOR MU? Kültegin Ögel, Figen Karadağ, Cüneyt Evren, Defne Tamar Gürol 1 Acibadem University Medical Faculty 2 Maltepe University Medical
(1971-1985) ARASI KONUSUNU TÜRK TARİHİNDEN ALAN TİYATROLAR
 ANABİLİM DALI ADI SOYADI DANIŞMANI TARİHİ :TÜRK DİLİ VE EDEBİYATI : Yasemin YABUZ : Yrd. Doç. Dr. Abdullah ŞENGÜL : 16.06.2003 (1971-1985) ARASI KONUSUNU TÜRK TARİHİNDEN ALAN TİYATROLAR Kökeni Antik Yunan
ANABİLİM DALI ADI SOYADI DANIŞMANI TARİHİ :TÜRK DİLİ VE EDEBİYATI : Yasemin YABUZ : Yrd. Doç. Dr. Abdullah ŞENGÜL : 16.06.2003 (1971-1985) ARASI KONUSUNU TÜRK TARİHİNDEN ALAN TİYATROLAR Kökeni Antik Yunan
Yarışma Sınavı A ) 60 B ) 80 C ) 90 D ) 110 E ) 120. A ) 4(x + 2) B ) 2(x + 4) C ) 2 + ( x + 4) D ) 2 x + 4 E ) x + 4
 1 4 The price of a book is first raised by 20 TL, and then by another 30 TL. In both cases, the rate of increment is the same. What is the final price of the book? 60 80 90 110 120 2 3 5 Tim ate four more
1 4 The price of a book is first raised by 20 TL, and then by another 30 TL. In both cases, the rate of increment is the same. What is the final price of the book? 60 80 90 110 120 2 3 5 Tim ate four more
ATILIM UNIVERSITY Department of Computer Engineering
 ATILIM UNIVERSITY Department of Computer Engineering COMPE 350 Numerical Methods Fall, 2011 Instructor: Fügen Selbes Assistant: İsmail Onur Kaya Homework: 1 Due date: Nov 14, 2011 You are designing a spherical
ATILIM UNIVERSITY Department of Computer Engineering COMPE 350 Numerical Methods Fall, 2011 Instructor: Fügen Selbes Assistant: İsmail Onur Kaya Homework: 1 Due date: Nov 14, 2011 You are designing a spherical
Gezgin İletişim Sistemleri
 Gezgin İletişim Sistemleri HÜCRESEL AĞLAR Cellular Networks Assoc. Prof. Hakan DOGAN Notlar 3 Devam Doç. Dr. Hakan DOGAN Büyük bir bahçenin sulamasını gerçekleştirmek için sabit ve her yöne su veren cihazlarımızın
Gezgin İletişim Sistemleri HÜCRESEL AĞLAR Cellular Networks Assoc. Prof. Hakan DOGAN Notlar 3 Devam Doç. Dr. Hakan DOGAN Büyük bir bahçenin sulamasını gerçekleştirmek için sabit ve her yöne su veren cihazlarımızın
www.imsamakina.com.tr
 HAKKIMIZDA 2003 Yılında ahşap modelhanesi olarak kurulan firmamız, müşteri taleplerini göz önünde bulundurarak ve bu talepleri günümüz teknolojisine uyarlayarak, bünyesine CNC dik işleme merkezleri katmıştır.
HAKKIMIZDA 2003 Yılında ahşap modelhanesi olarak kurulan firmamız, müşteri taleplerini göz önünde bulundurarak ve bu talepleri günümüz teknolojisine uyarlayarak, bünyesine CNC dik işleme merkezleri katmıştır.
d h k d t s a t
 1 t d h k d, t t s a t 2 TS EN ISO / IEC 17065 Uygunluk Değerlendirmesi standardına uygun olarak ve akreditasyon kapsamında gerçekleştirilen kalite yönetim sistemi ve ürün belgelendirme programına bağlı
1 t d h k d, t t s a t 2 TS EN ISO / IEC 17065 Uygunluk Değerlendirmesi standardına uygun olarak ve akreditasyon kapsamında gerçekleştirilen kalite yönetim sistemi ve ürün belgelendirme programına bağlı
NOKTA VE ÇİZGİNİN RESİMSEL ANLATIMDA KULLANIMI Semih KAPLAN SANATTA YETERLİK TEZİ Resim Ana Sanat Dalı Danışman: Doç. Leyla VARLIK ŞENTÜRK Eylül 2009
 NOKTA VE ÇİZGİNİN RESİMSEL ANLATIMDA KULLANIMI SANATTA YETERLİK TEZİ Resim Ana Sanat Dalı Danışman: Doç. Leyla VARLIK ŞENTÜRK Eylül 2009 Anadolu Üniversitesi Güzel Sanatlar Enstitüsü Eskişehir RESİMSEL
NOKTA VE ÇİZGİNİN RESİMSEL ANLATIMDA KULLANIMI SANATTA YETERLİK TEZİ Resim Ana Sanat Dalı Danışman: Doç. Leyla VARLIK ŞENTÜRK Eylül 2009 Anadolu Üniversitesi Güzel Sanatlar Enstitüsü Eskişehir RESİMSEL
12-15 YAŞ ARASI ANTRENMANLI ÇOCUKLARDA CiNSiYET VE YAŞıN LAKTAT VE KALP ATIM HIZI CEVAPLARINA ETKisi
 Spor Bilimleri Dergisi Hacettepe 1. ofsport Sciences 2005,16 (1),1-18 12-15 YAŞ ARASI ANTRENMANLI ÇOCUKLARDA CiNSiYET VE YAŞıN LAKTAT VE KALP ATIM HIZI CEVAPLARINA ETKisi Alper GÜVENÇ, Rıdvan ÇOLAK, Caner
Spor Bilimleri Dergisi Hacettepe 1. ofsport Sciences 2005,16 (1),1-18 12-15 YAŞ ARASI ANTRENMANLI ÇOCUKLARDA CiNSiYET VE YAŞıN LAKTAT VE KALP ATIM HIZI CEVAPLARINA ETKisi Alper GÜVENÇ, Rıdvan ÇOLAK, Caner
İstanbul a Hoşgeldiniz
 Welcome To Istanbul İstanbul a Hoşgeldiniz CHIC Accessories Administration Office CHIC Tekstil ve Metal would like to welcome you to Turkey! Our company s aim is to offer our clients complete branding
Welcome To Istanbul İstanbul a Hoşgeldiniz CHIC Accessories Administration Office CHIC Tekstil ve Metal would like to welcome you to Turkey! Our company s aim is to offer our clients complete branding
Dairesel grafik (veya dilimli pie chart circle graph diyagram, sektor grafiği) (İngilizce:"pie chart"), istatistik
 DAİRESEL GRAFİK Dairesel grafik (veya dilimli diyagram, sektor grafiği) (İngilizce:"pie chart"), istatistik biliminde betimsel istatistik alanında kategorik (ya sırasal ölçekli ya da isimsel ölçekli) verileri
DAİRESEL GRAFİK Dairesel grafik (veya dilimli diyagram, sektor grafiği) (İngilizce:"pie chart"), istatistik biliminde betimsel istatistik alanında kategorik (ya sırasal ölçekli ya da isimsel ölçekli) verileri
Theory of Dimensioning
 Theory of Dimensioning In general, the description of shape and size together gives complete information for producing the object represented. The dimensions put on the drawing are those required for the
Theory of Dimensioning In general, the description of shape and size together gives complete information for producing the object represented. The dimensions put on the drawing are those required for the
